
















Ecorestoration of Sikanderpur forest
Ecorestoration of Sikanderpur forest
Ecorestoration of Sikanderpur forest
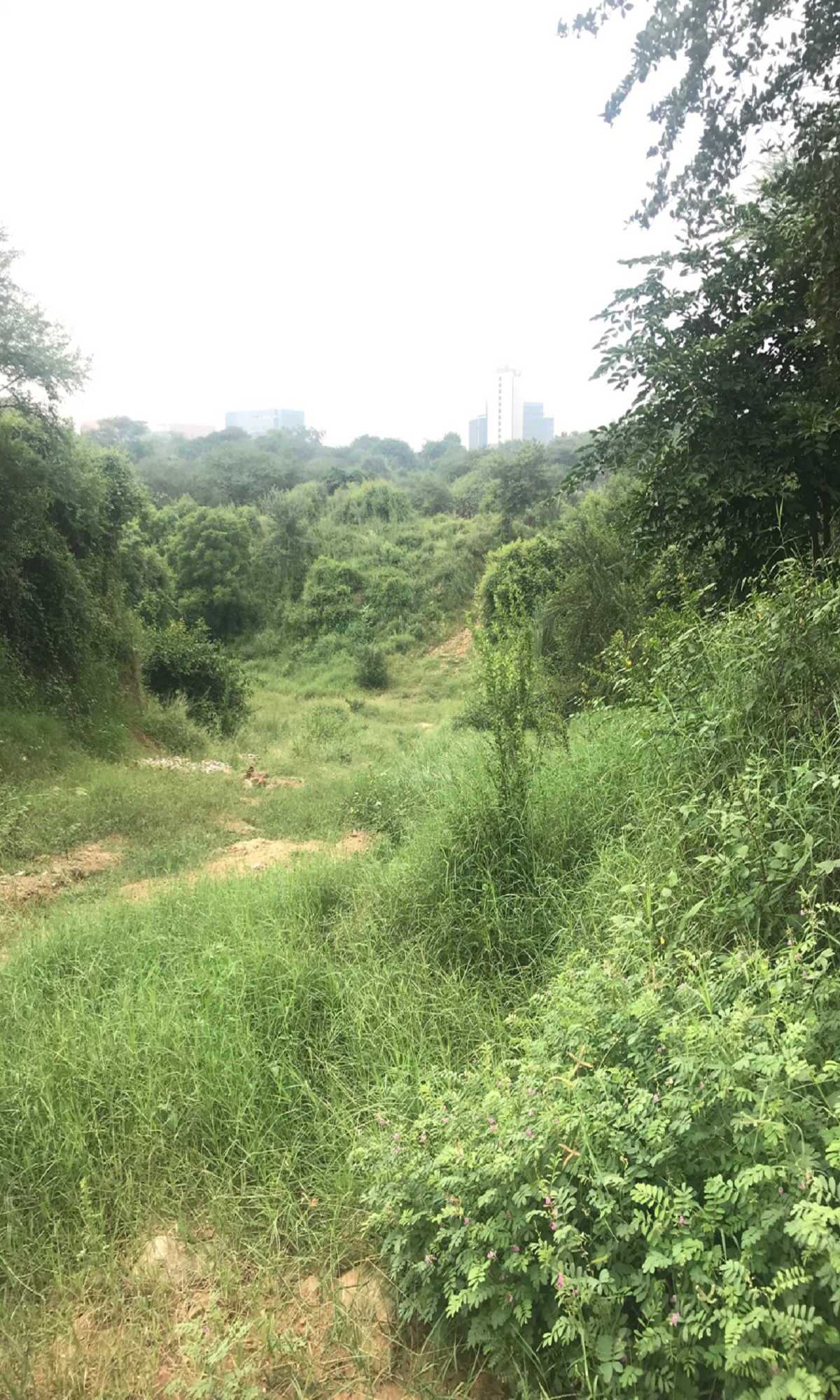
Gurugram is a classic example of an unplanned rapid urbanisation.
The Aravallis, one of the oldest mountain ranges come right into the city as ridge forests.
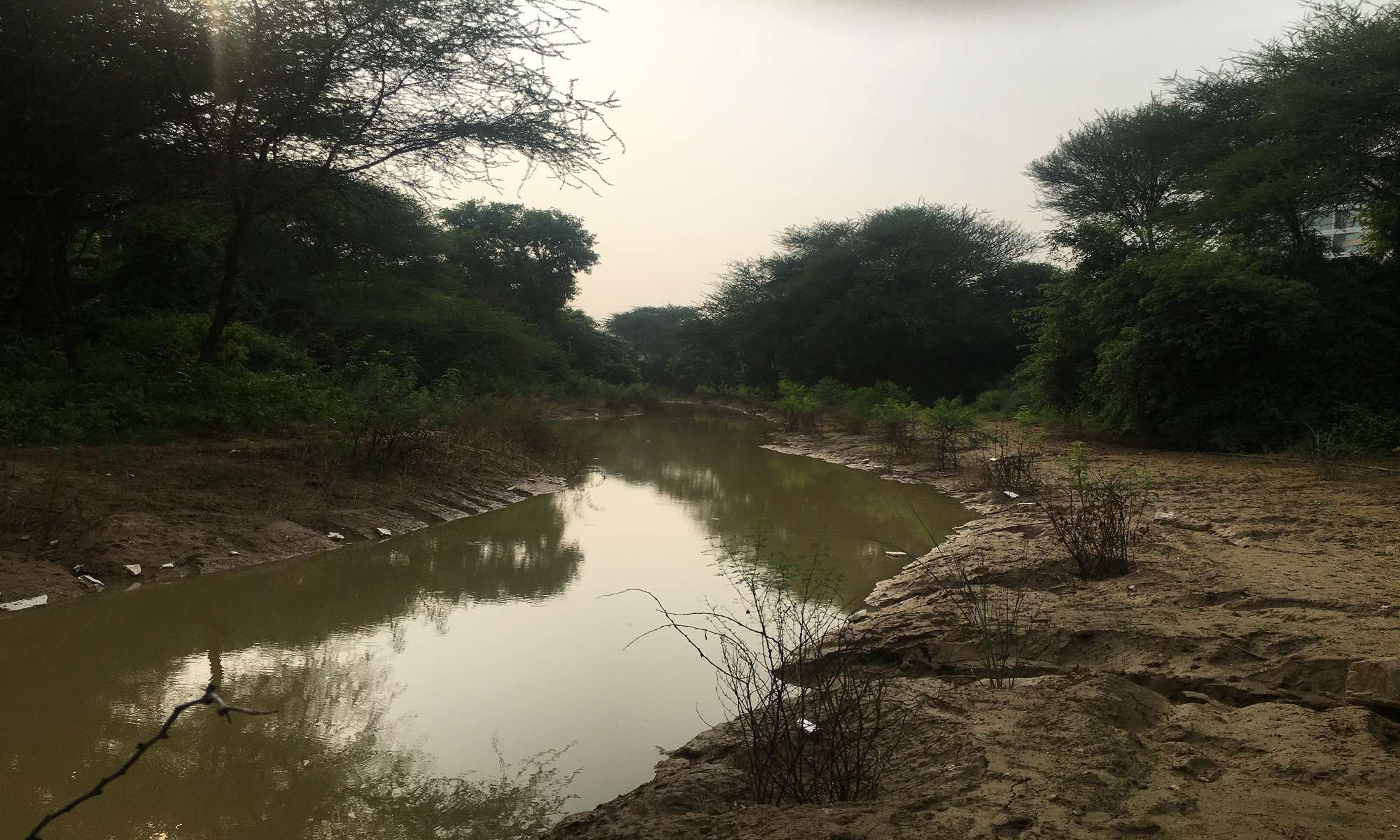
Storm water runoff from the hills and the plains was getting collected in ponds and lakes.
Development without regard to context and filled up ponds, led to huge waterlogging issues during monsoons, while groundwater has shrunk. Air pollution and shrinking greens are other concerns.
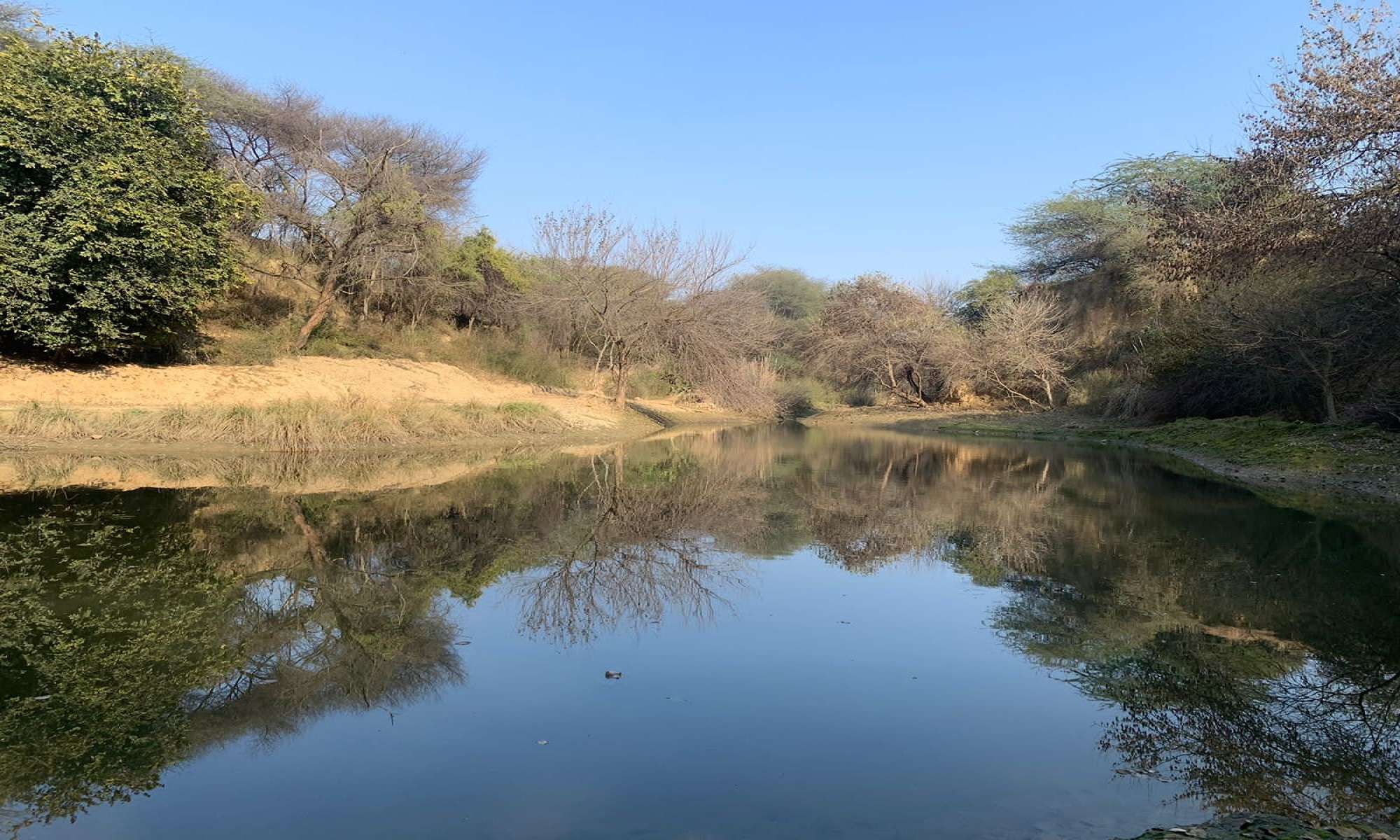
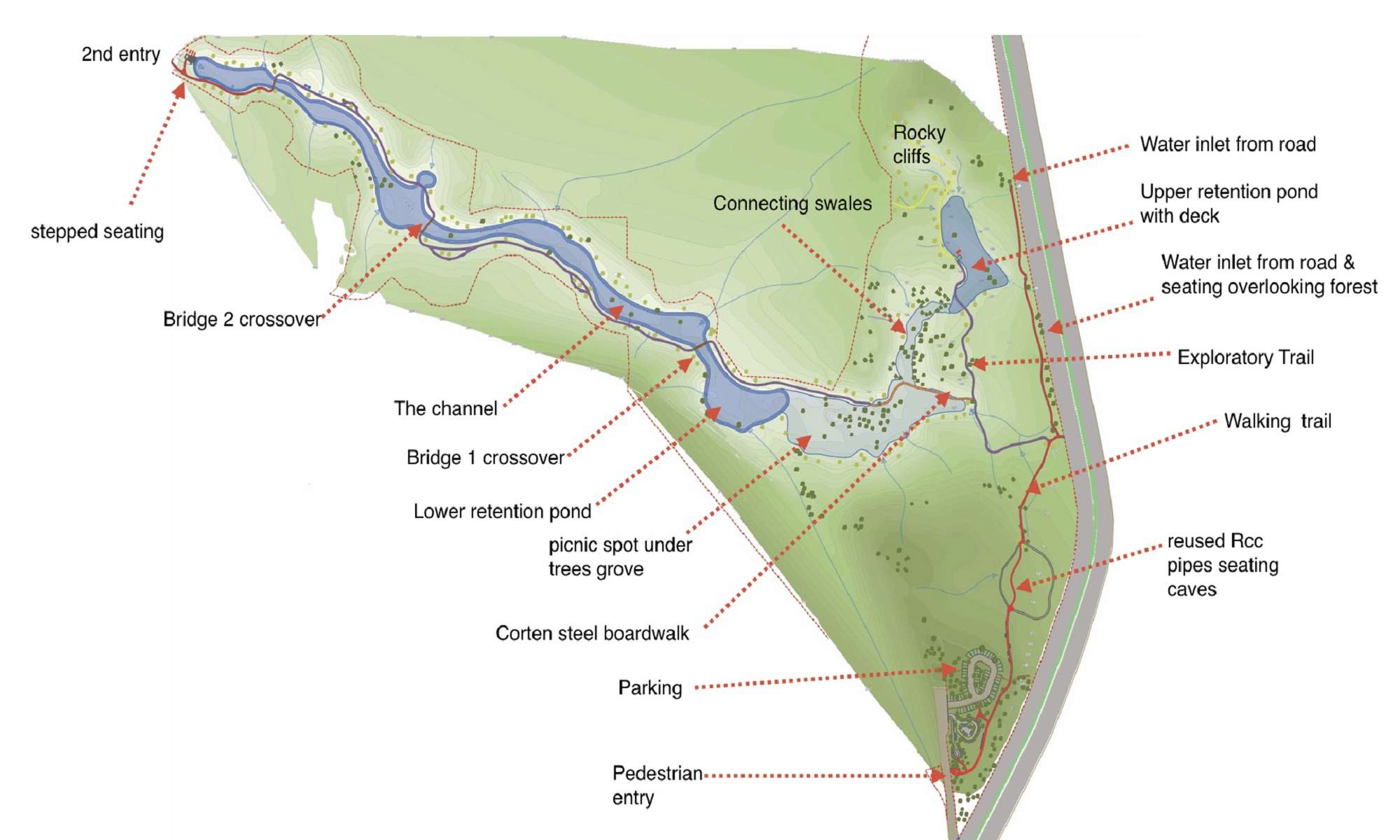
Our site is a part of the ridge forest. It was an abandoned stone quarry which turned to a construction waste dumpyard.
Our objective was to restore the degraded forest, protecting and enhancing the biodiversity, while inspiring human reconnection to the natural rhythms of the forest.
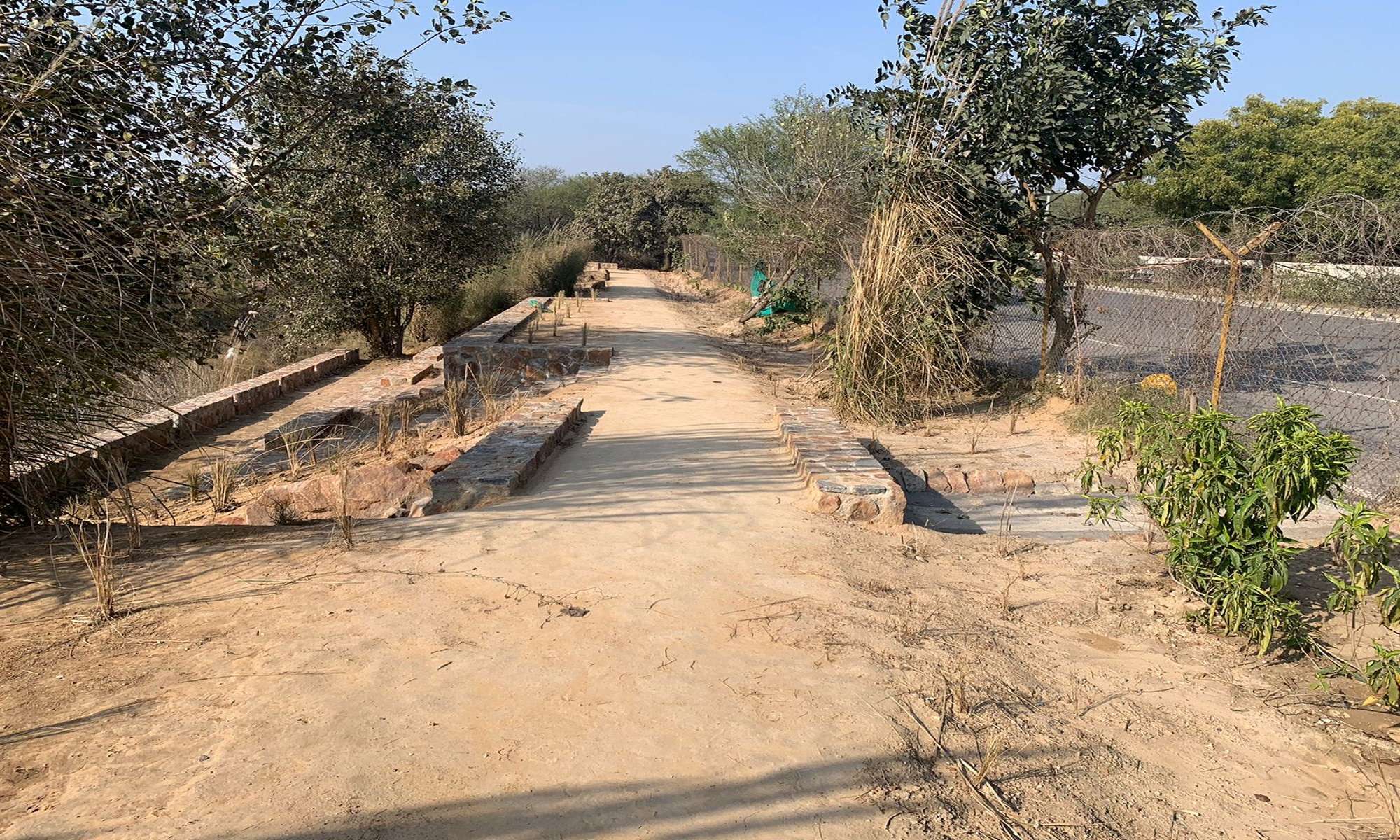
We started with study and analysis of the character and experience potential of the site.
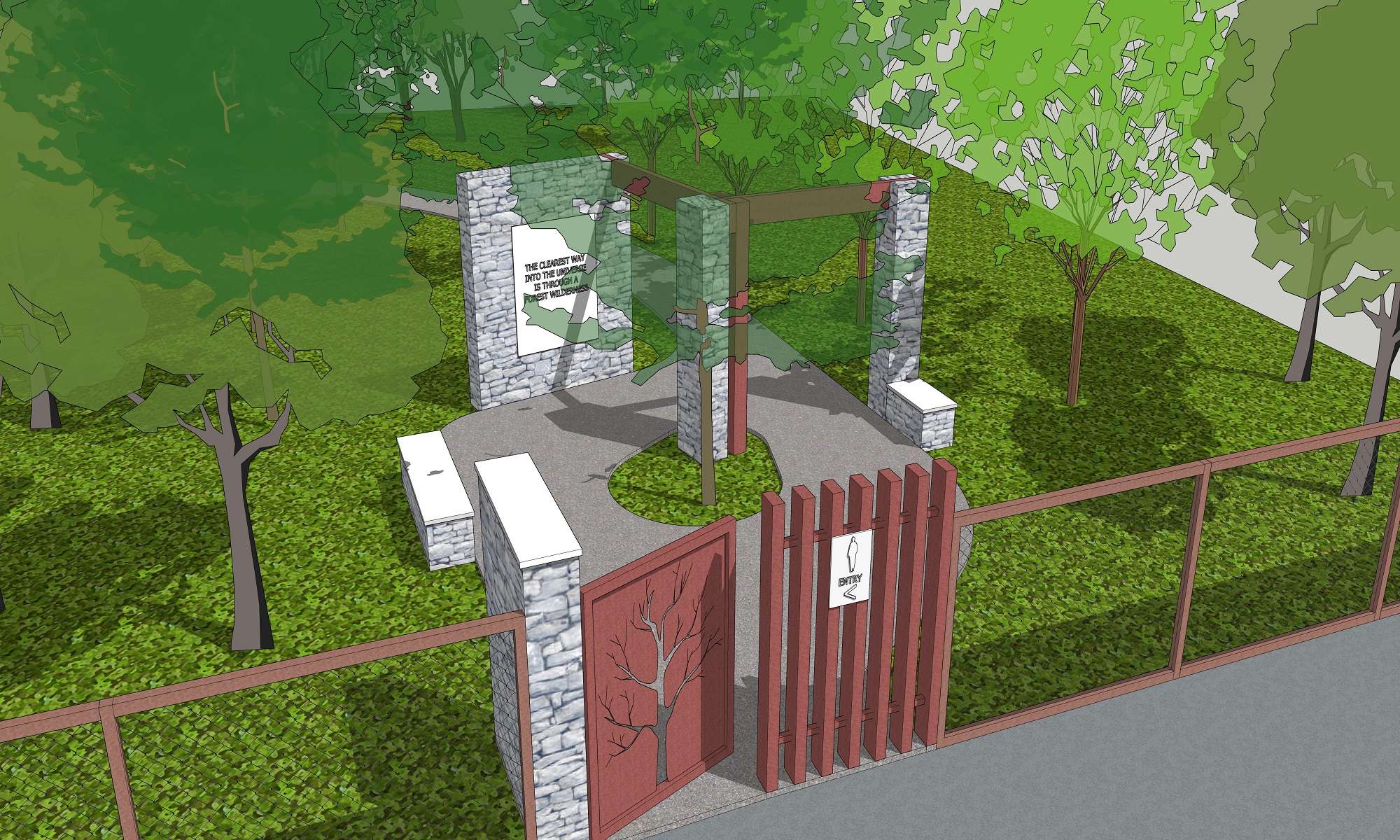
We identified entry points, trails, rest points and waterflow patterns.
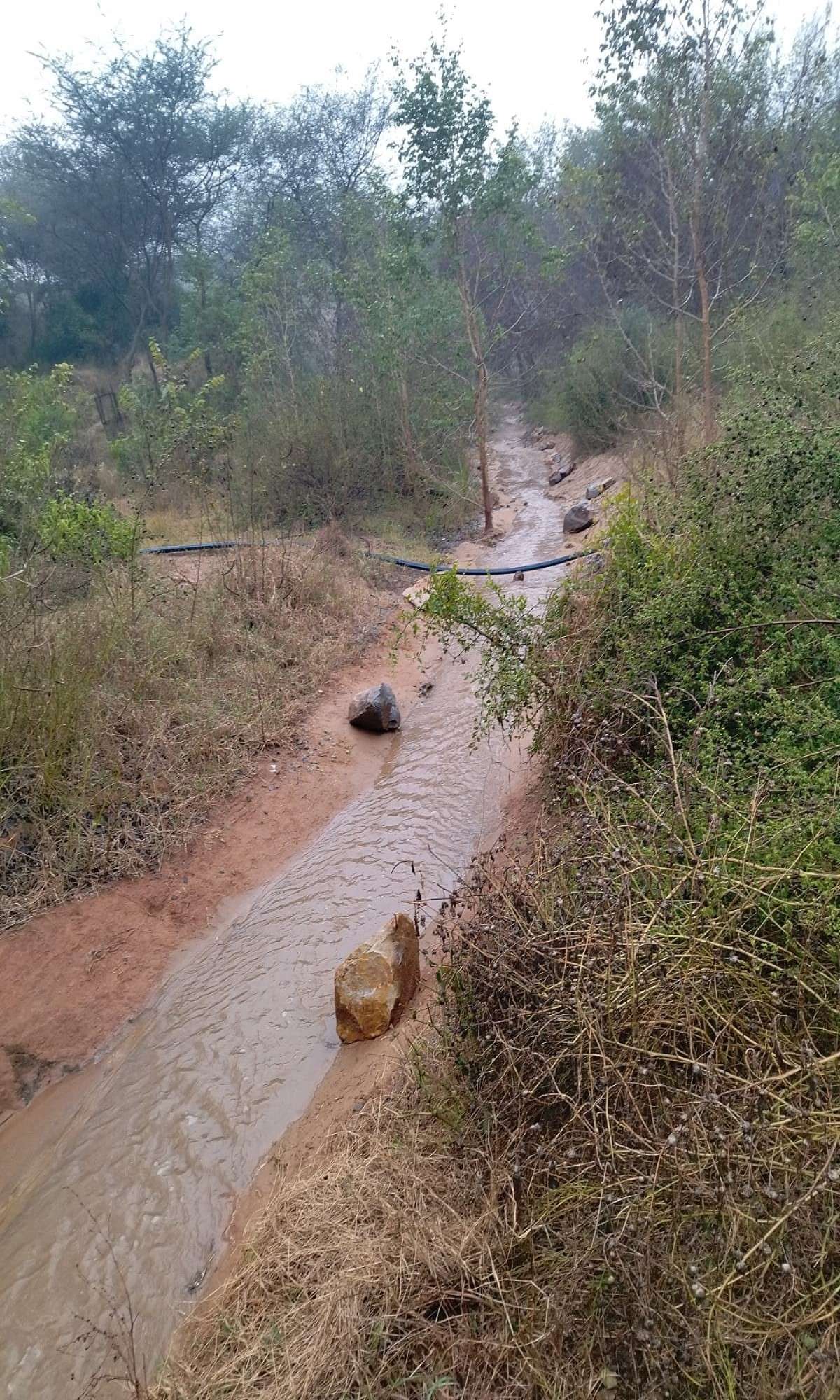
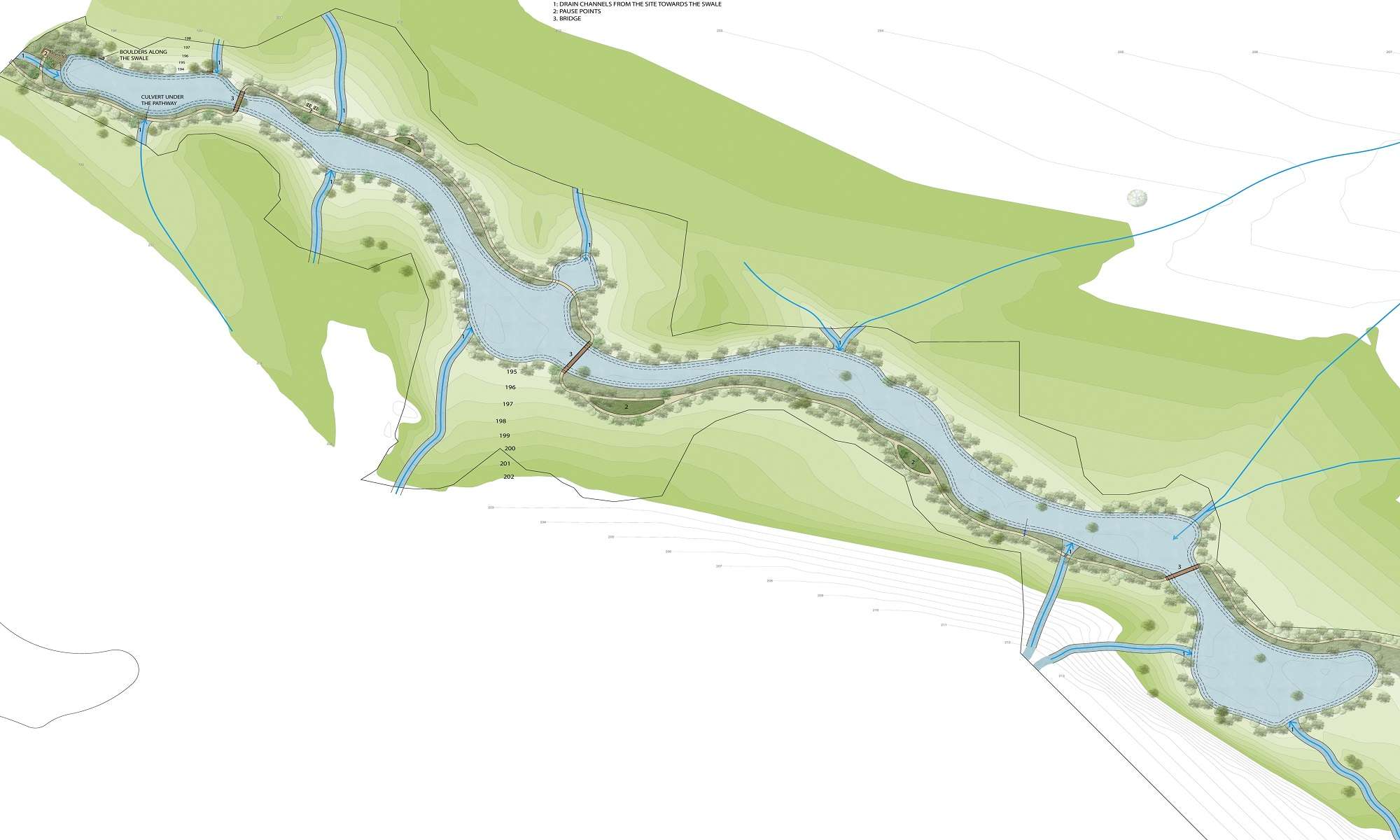
For storm water management, we
• Diverted water from adjacent roads
• Increased water retention capacity of the forest, recharging groundwater
• mitigated soil erosion by introducing boulders as breakers in the waterflow.
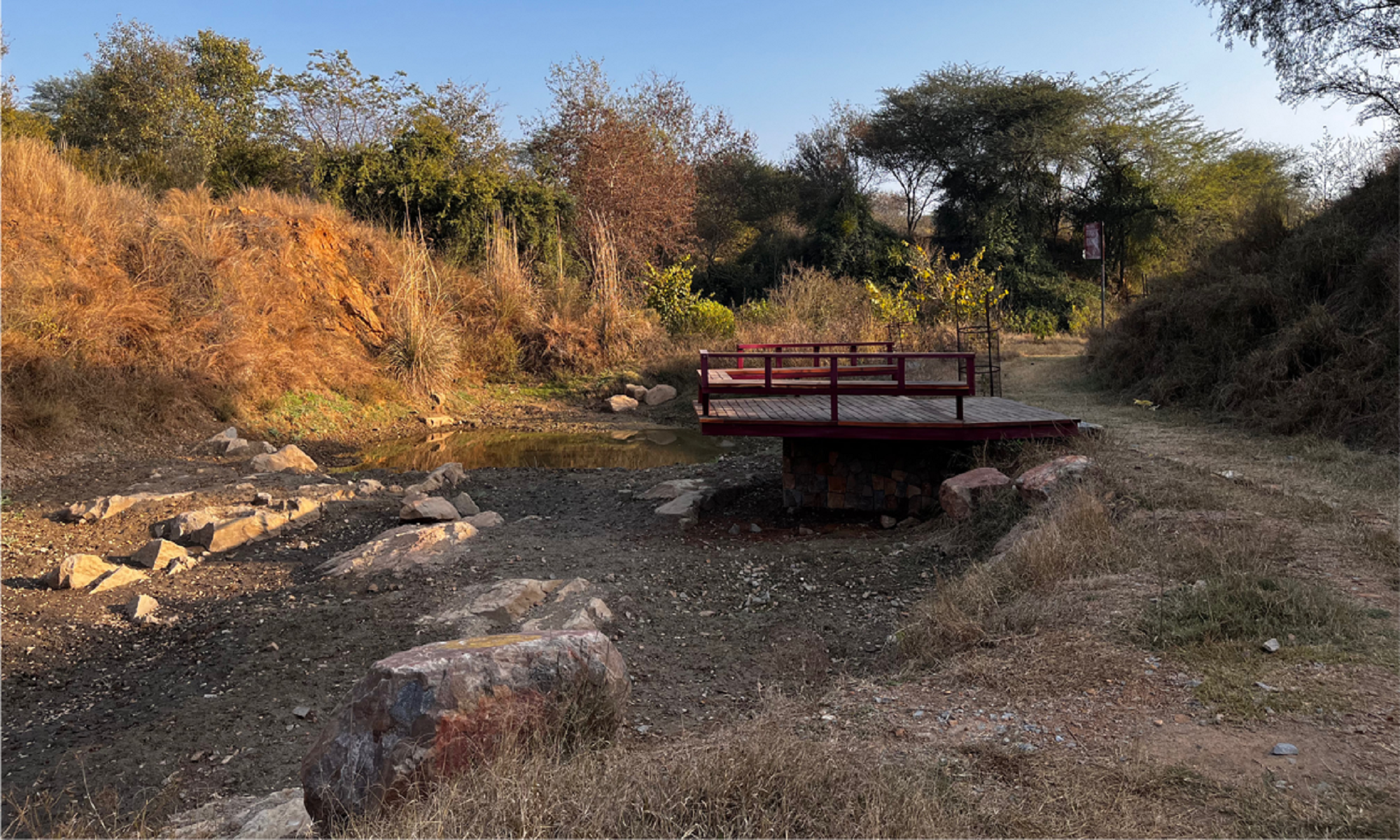
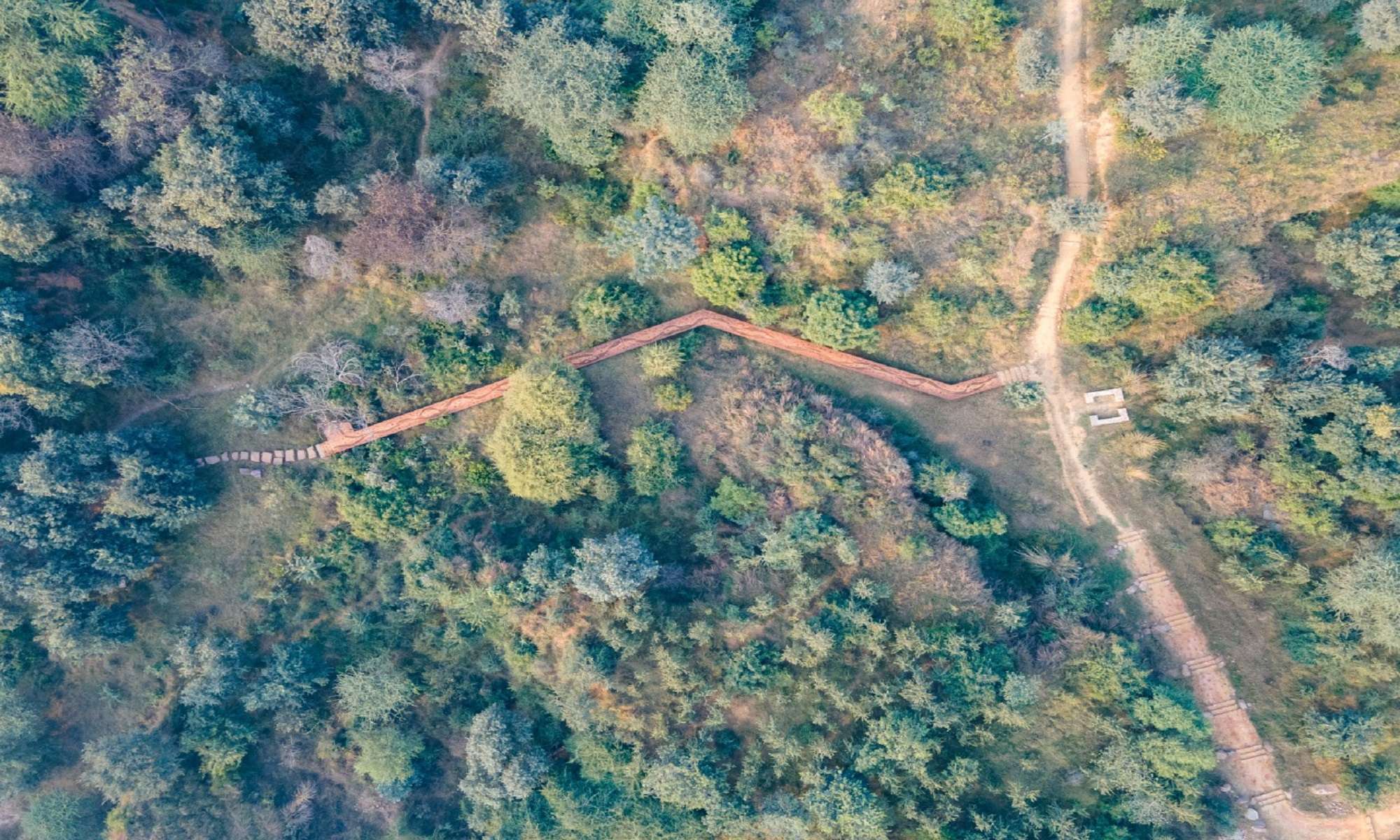
• created a large pond in a rocky part of the site, which is connected through swales to a lower pond which will house waterlilies.
Further to this pond is a wide, connecting water channel , about a km long.
For social and spatial placemaking features, we have introduced
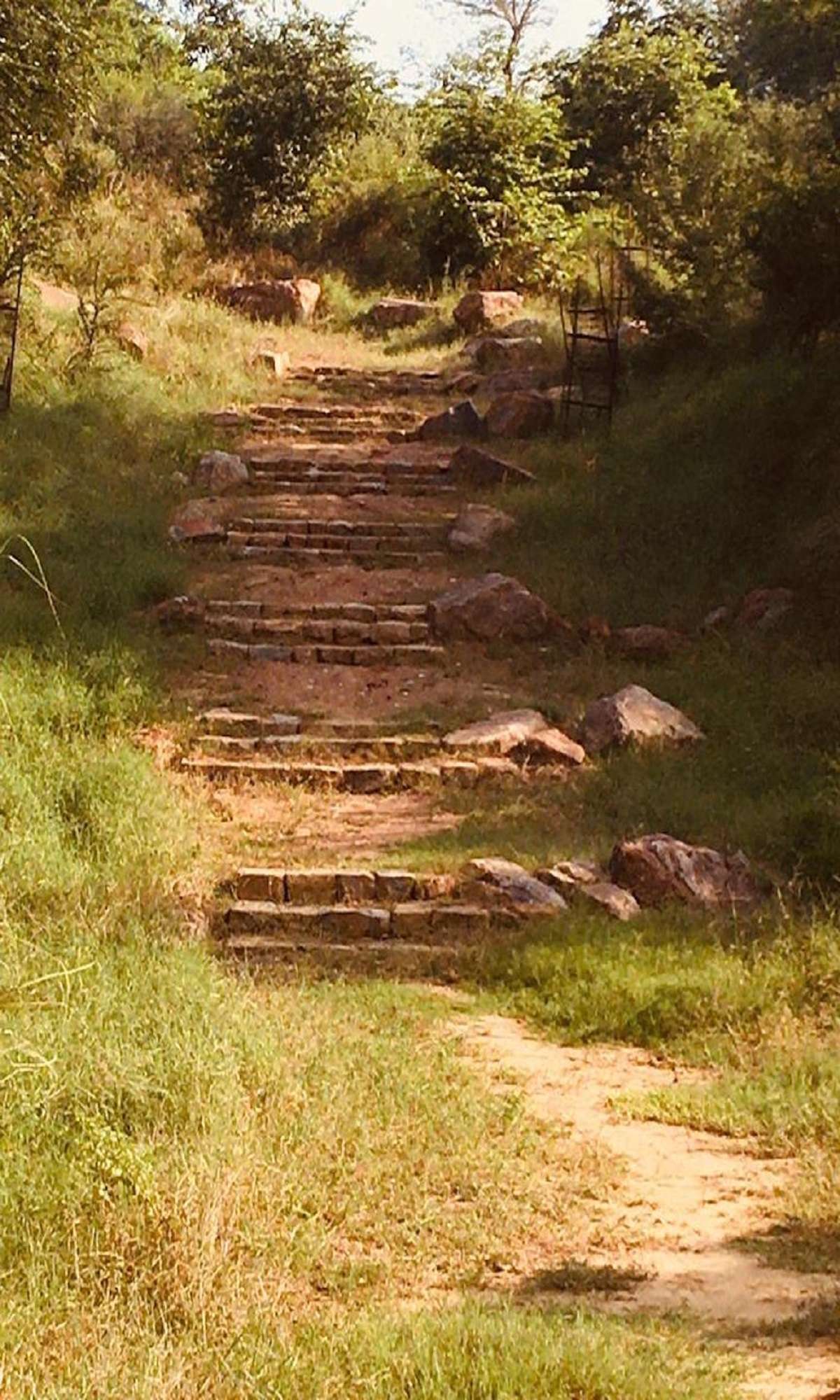
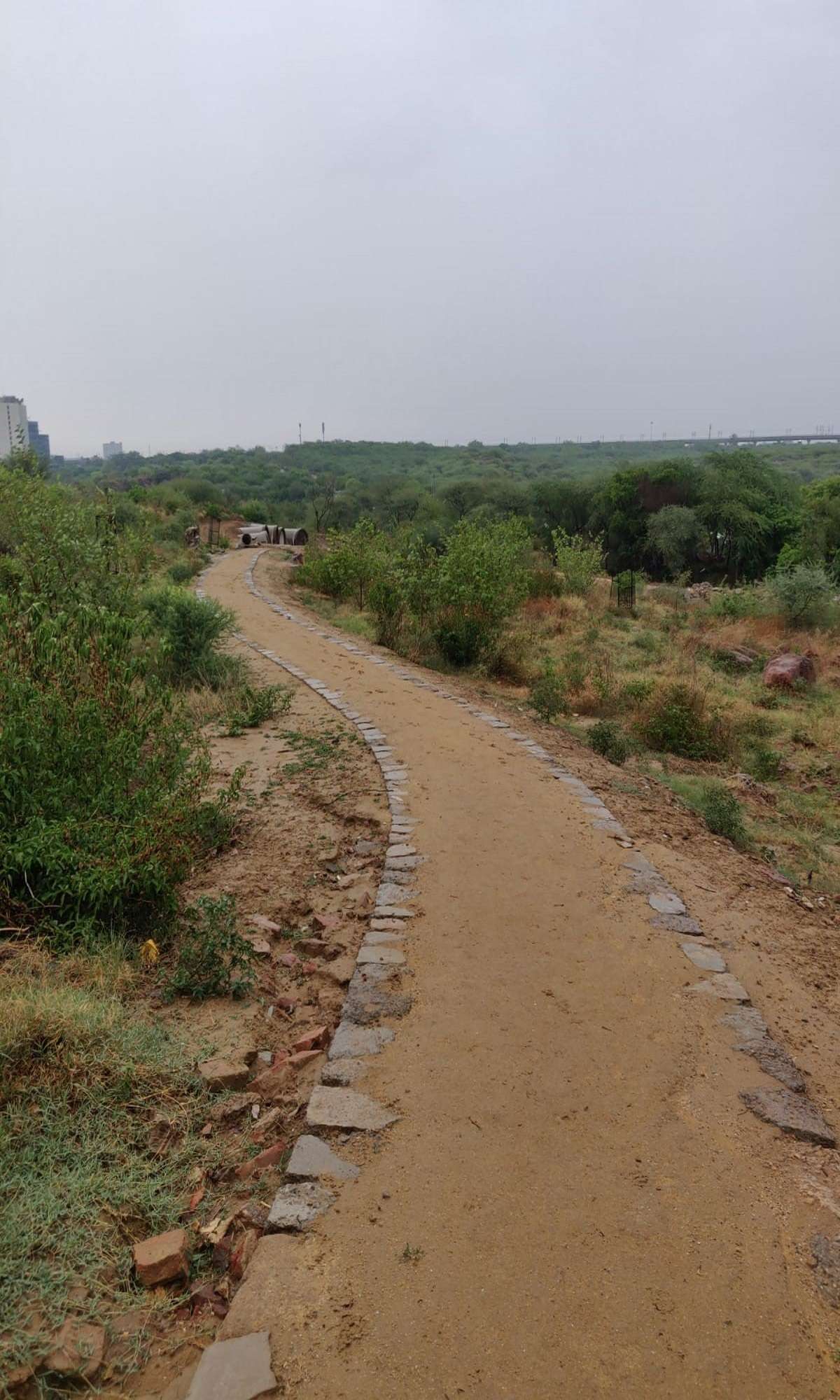
• Trails
-for all agegroups ,with sit outs.
- to explore the forest and experience richness of spaces and views.
- to explore more challenging terrain
• Deck at the rocky pond, and a sunset point after a short steep climb that is rejuvenating.
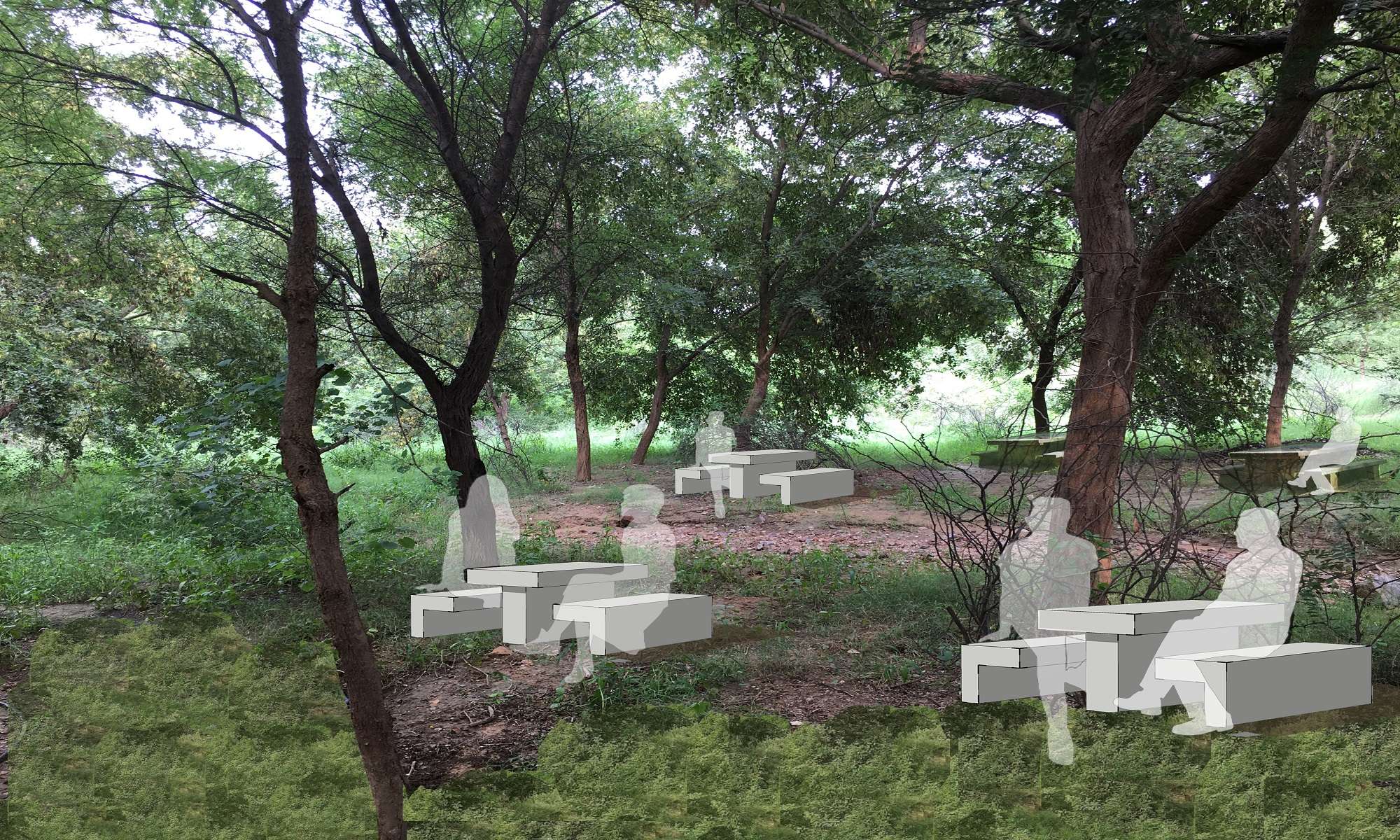
• a picnic sit out cluster under an existing tree grove
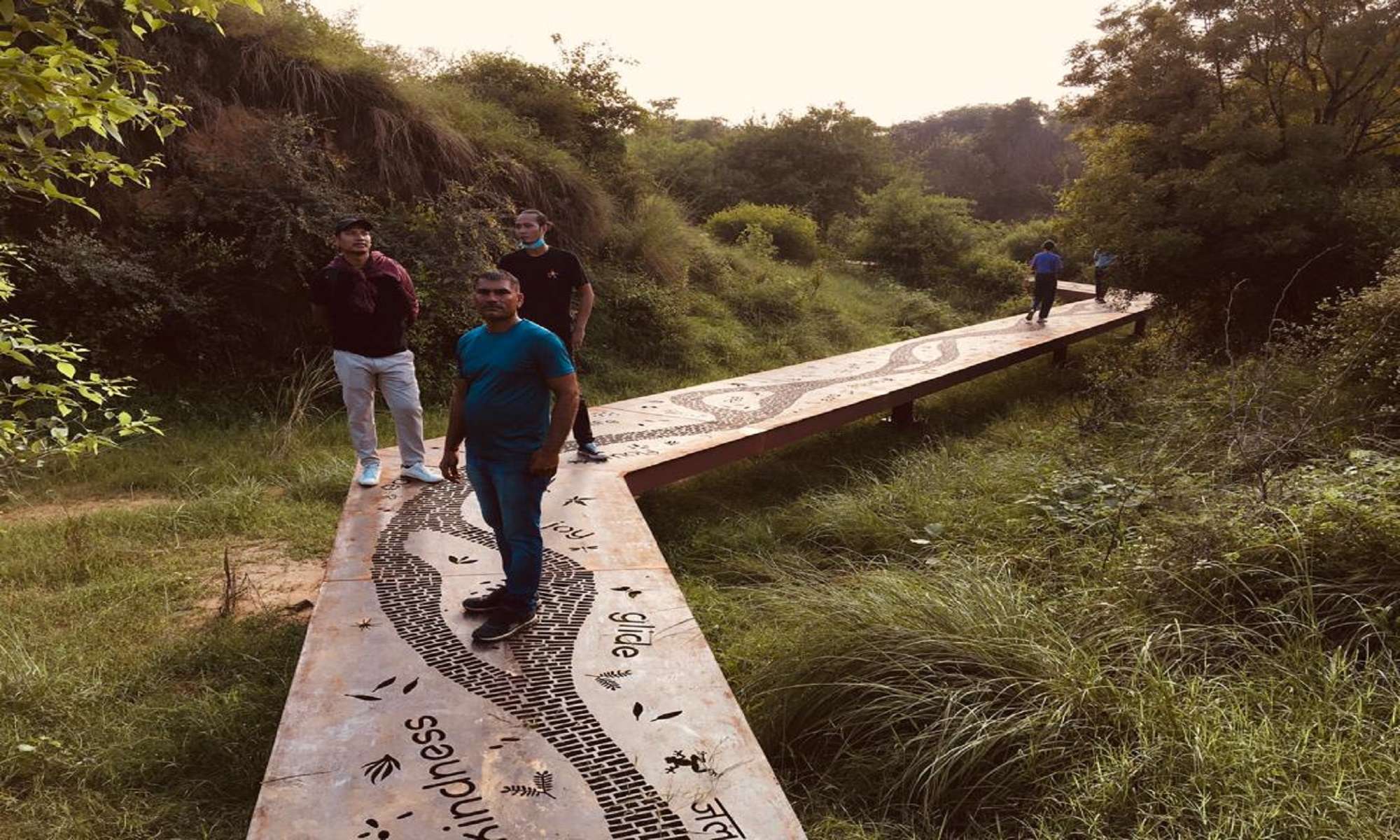
• Boardwalk in corten steel across a low-lying valley
• bridges across water channel
For materials except for metal, we used
1. loose stones from the forest, left from the quarrying activity
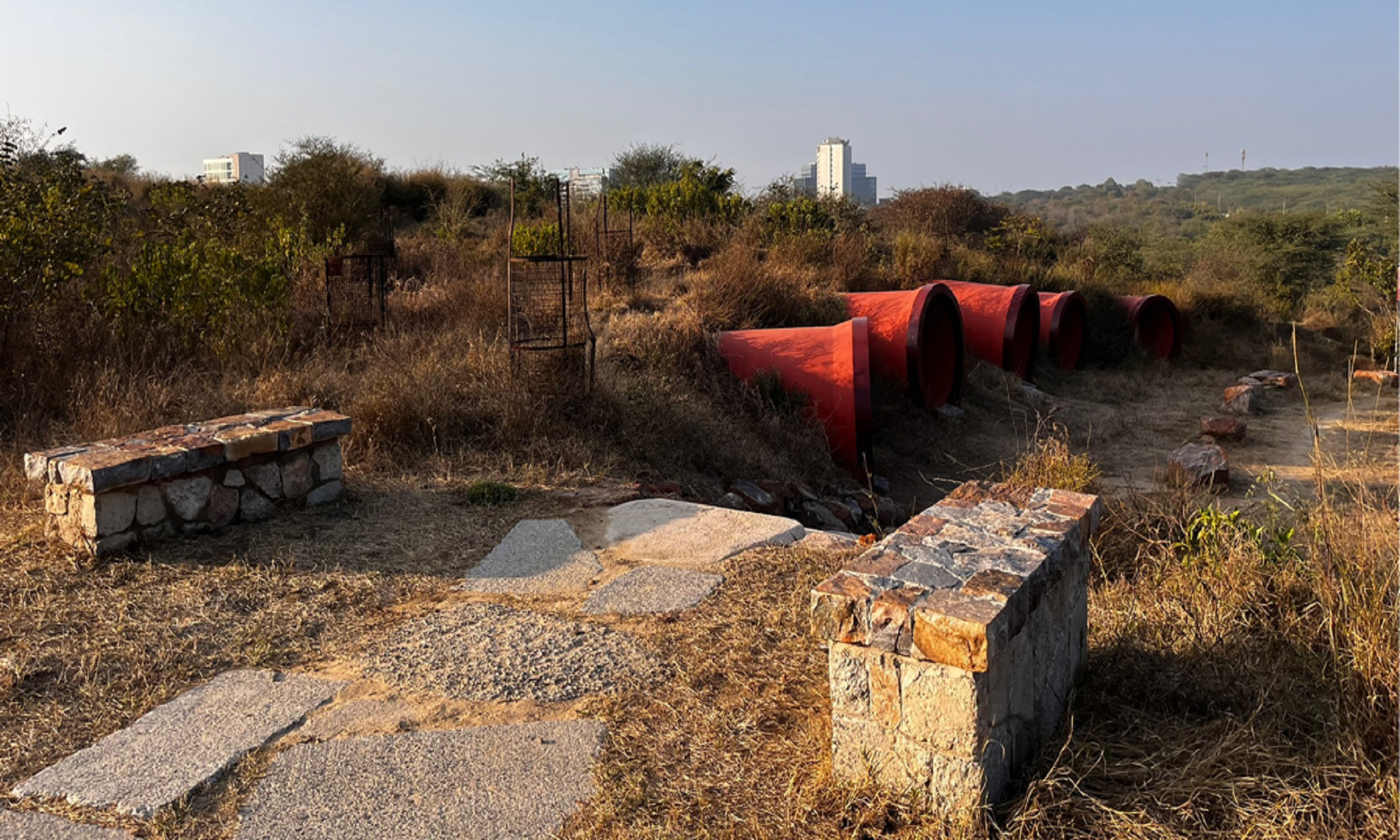
2. Construction debris lying on the site, used to make walls and for base layers of paved areas. 5 big dumped RCC pipes were reused to retain soil along a steep slope as well as to function as colorful seating caves.
4. Paths were of beaten soil.
5. The deck was constructed with wood from an invasive tree being phased out.
By employing these strategies and materials, we have successfully revitalized the forest while preserving its unique features and promoting a harmonious coexistence between people and nature.
This project is in the model of public private partnership. It is a public realm project accessible to all people. It has been developed by a citizen's group NGO, utilising 'Corporate Social Responsibility' funds. They were entrusted by the city development authority and will be maintaining for two years minimum before handing over the upkeep.
It has been inaugurated by the Chief minister of Haryana State.
The project intent has been to restore the degraded forest, using only indigenous plants, while making it accessible to people. The forest area with its undulating topography was an opportunity to use it as a sponge for the city stormwater.
