














MILE
MILE
22@ Barcelona: Espais exteriors i cobertes de l’edifici MILE
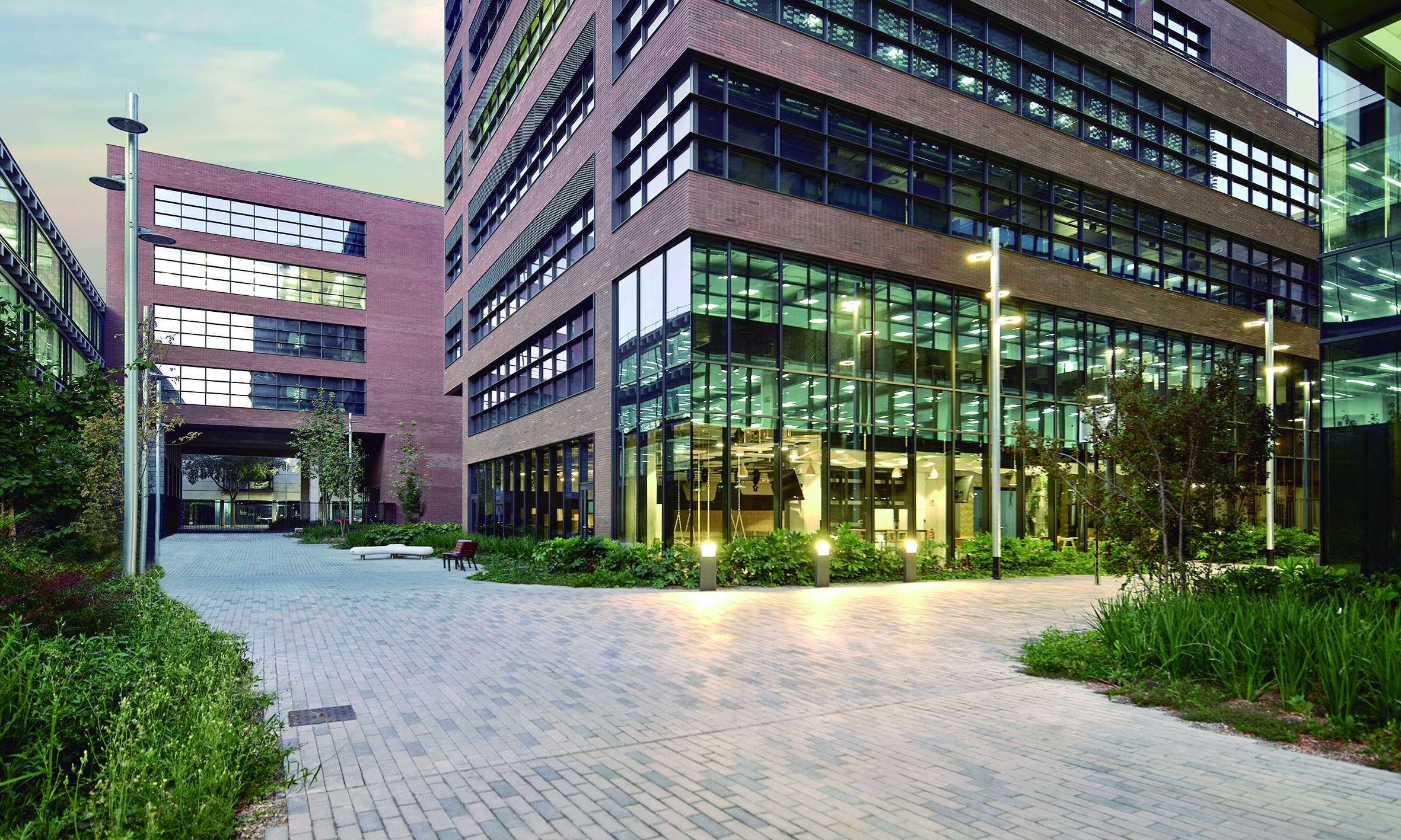
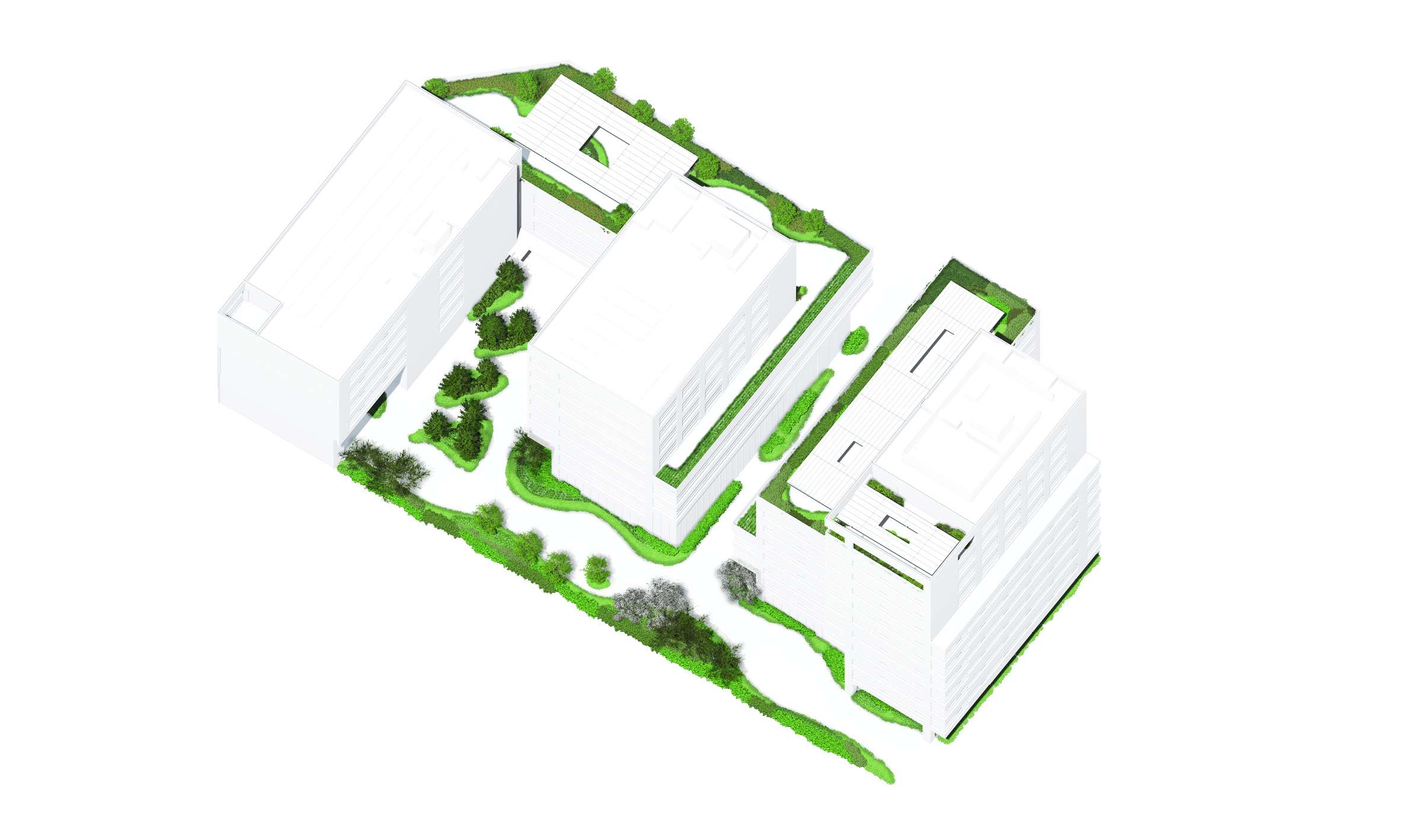
The MILE building is an office complex in Barcelona’s 22@ district, occupying two-thirds of a typical Cerdà Eixample block. Our client commissioned us to intervene in the public spaces surrounding the complex, as well as on the terraces and rooftops created by the architectural volume.
The project is located in the 22@ neighbourhood, an area with an industrial past that still influences its current appearance. In recent years, it has undergone a major transformation marked by the introduction of new building typologies that accommodate emerging uses and programs, blending residential living with offices for tech companies.
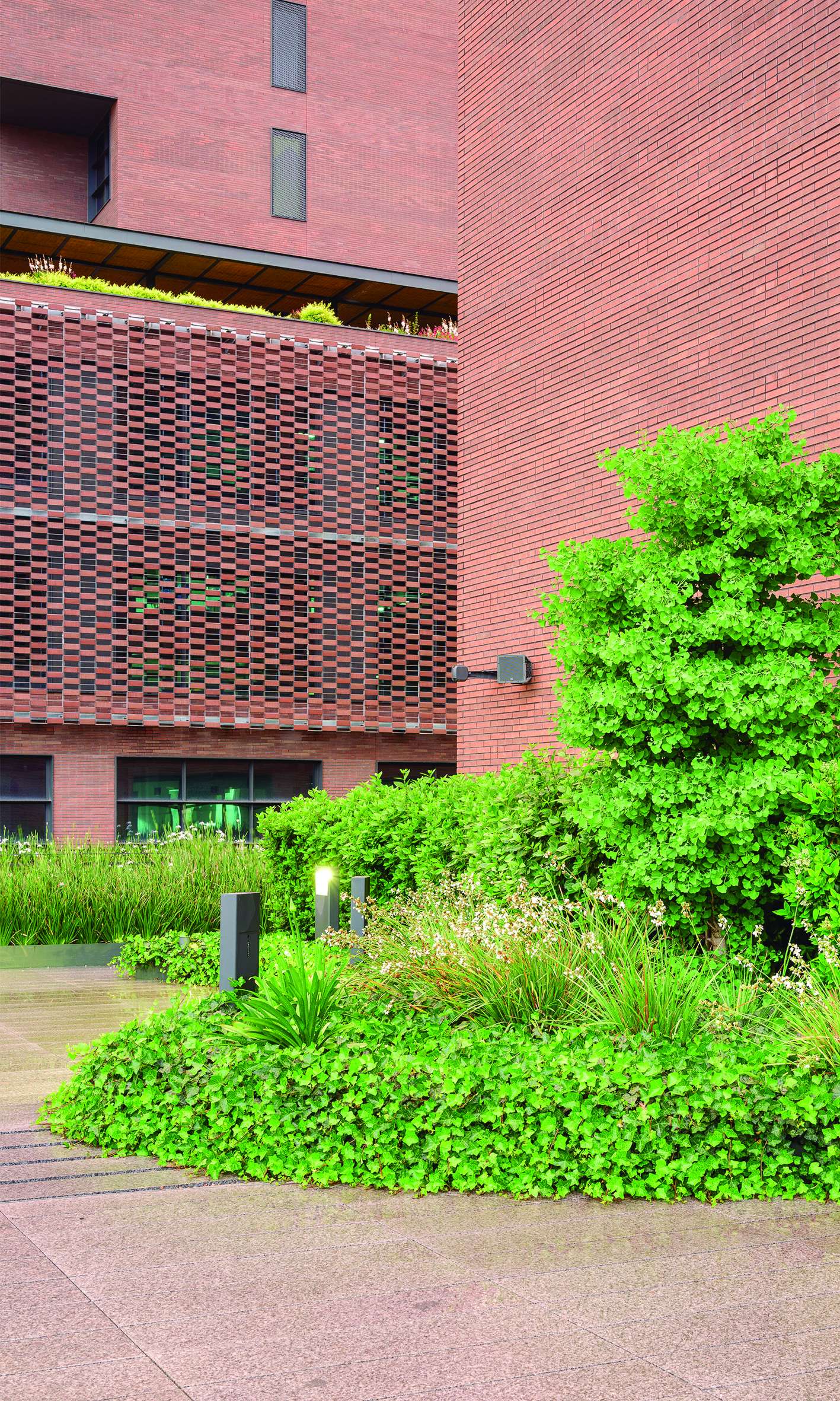
Our intervention promotes a symbiotic relationship between vegetation and architecture, always applied to a certified green roof system that ensures long-term viability. The main goal has been to integrate vegetation into the architectural volume to provide users with the comfort of an urban garden. At the same time, this garden helps to mitigate the “urban heat island” effect, thereby enhancing the well-being and comfort of its users.
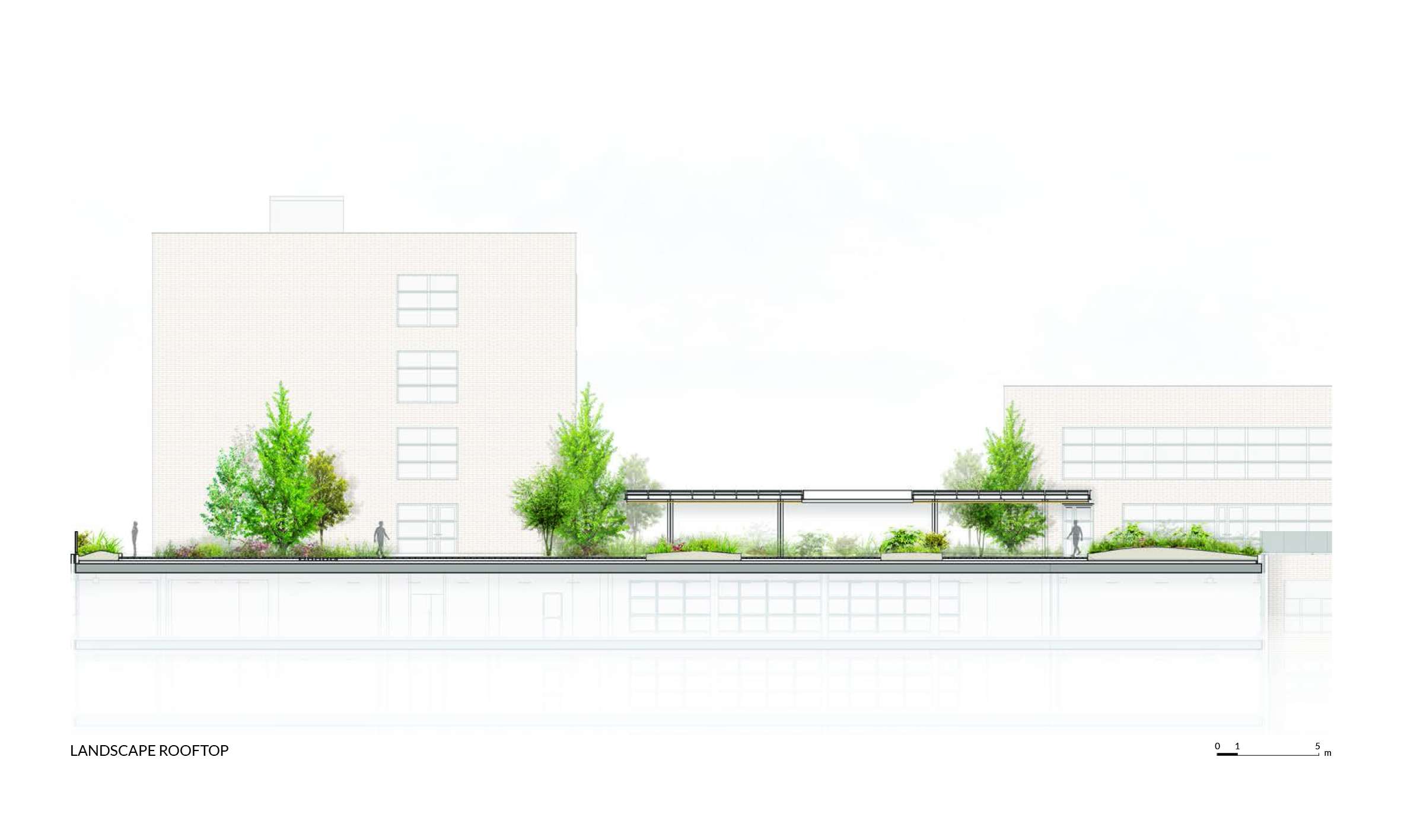
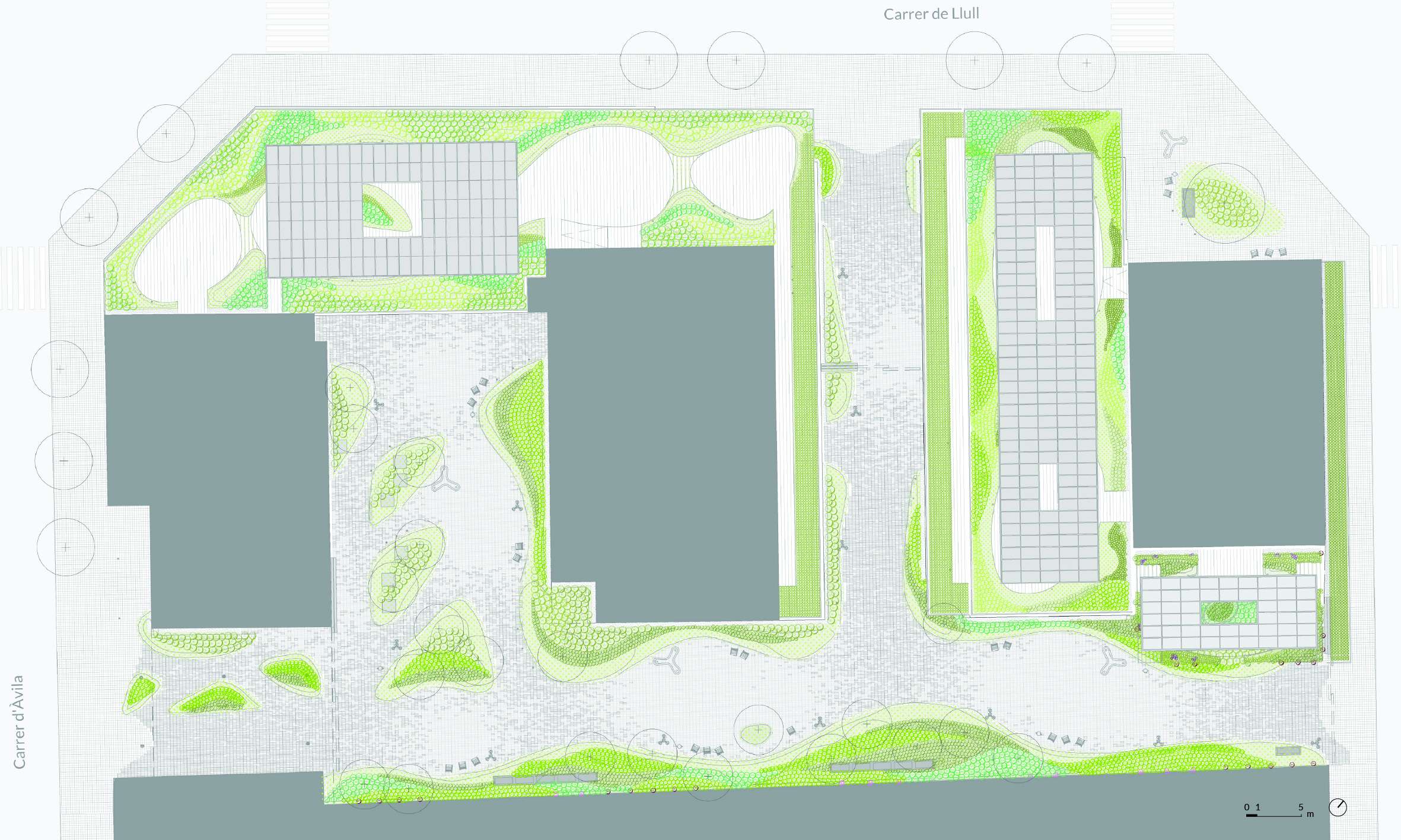
The project works across two main areas. First, the intervention in the public space at ground level, surrounded by the various built volumes—an area intended for circulation, connection, and gathering for both the public and the building’s users. Second, the landscape design of the rooftops created by the building’s volume, located at different levels and conceived as genuine open-air office spaces.
The design naturalizes these spaces by blending them with the surrounding architecture, creating a real sense of continuity with the adjacent streets and ensuring seamless integration with the urban environment.
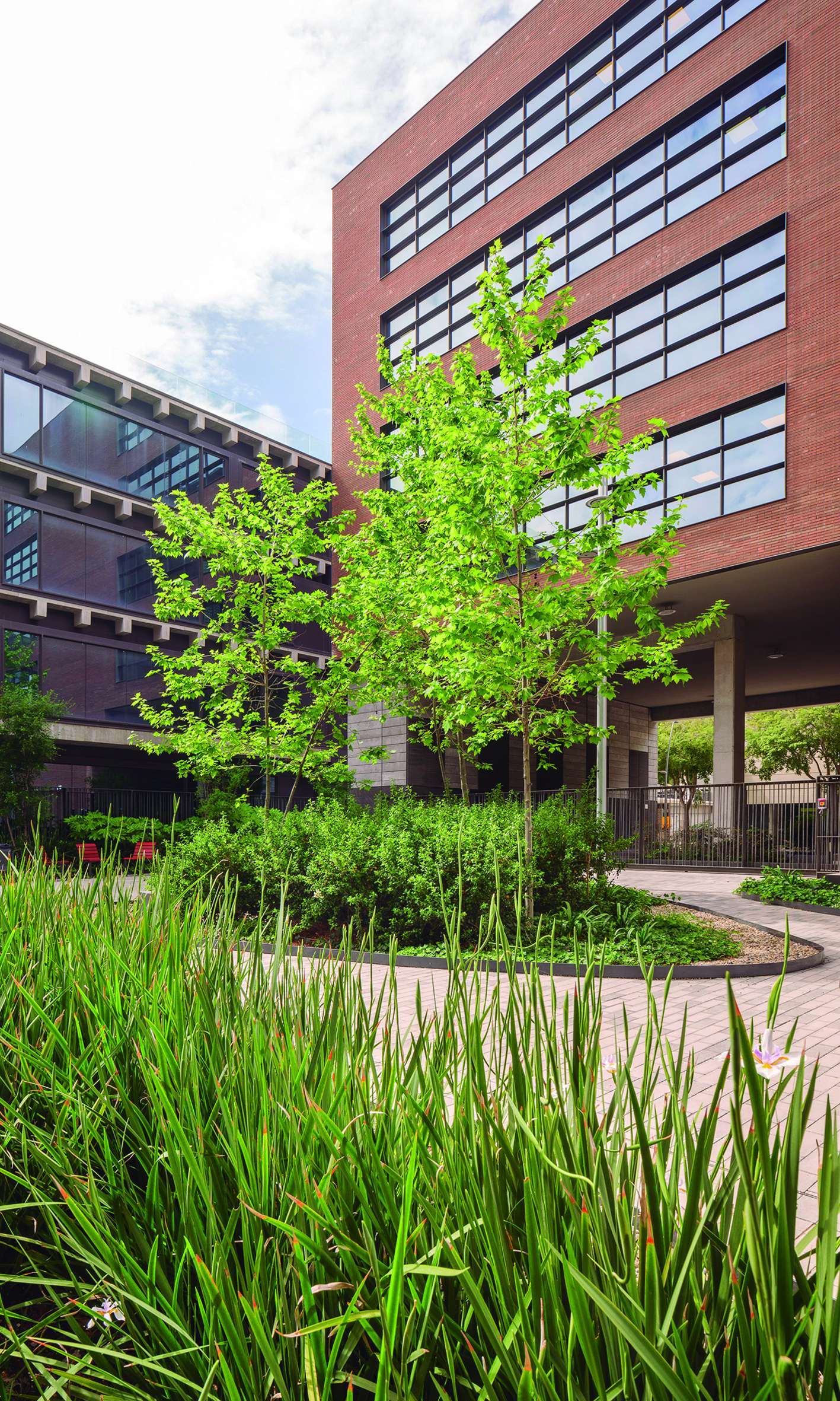
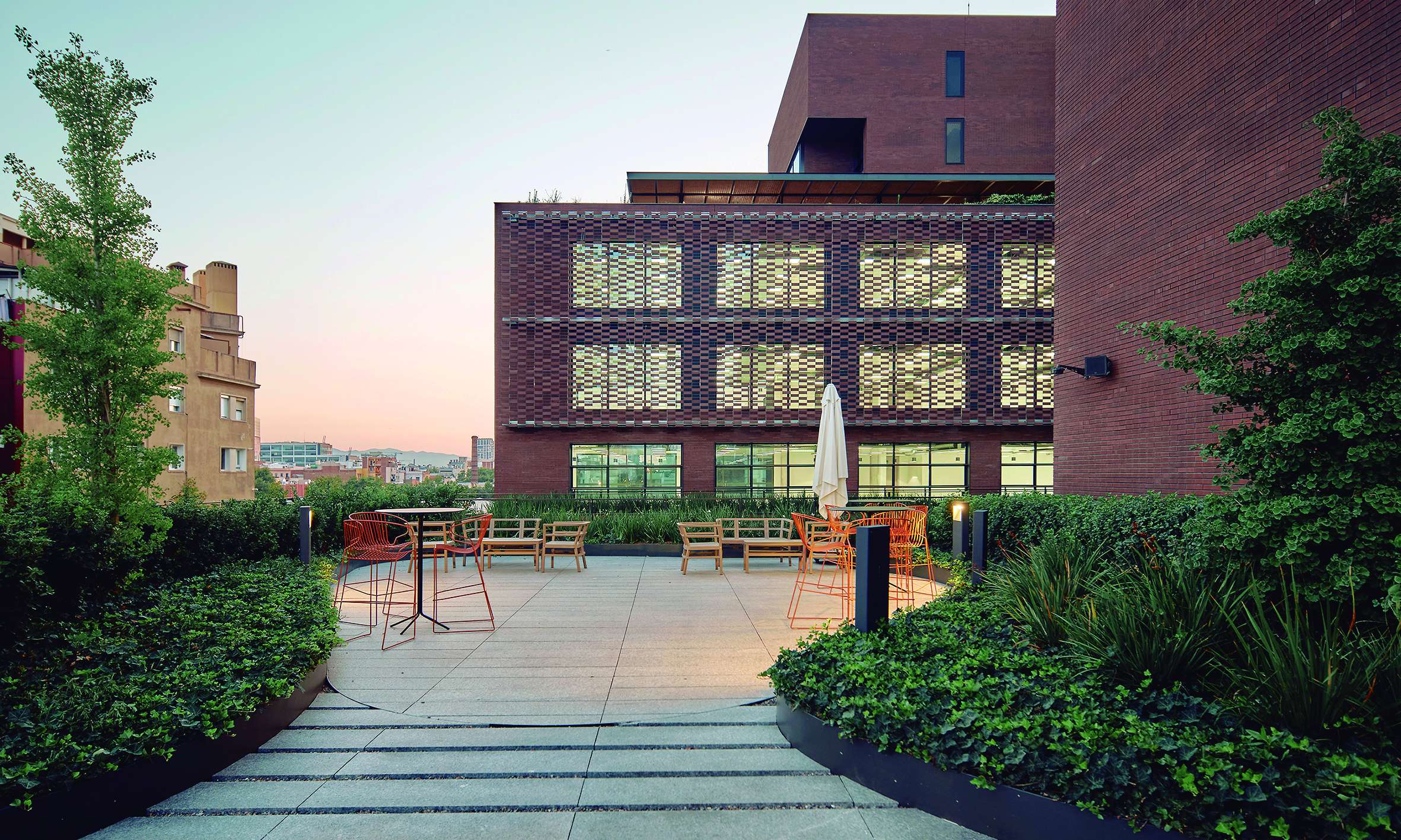
The Interior Courtyard
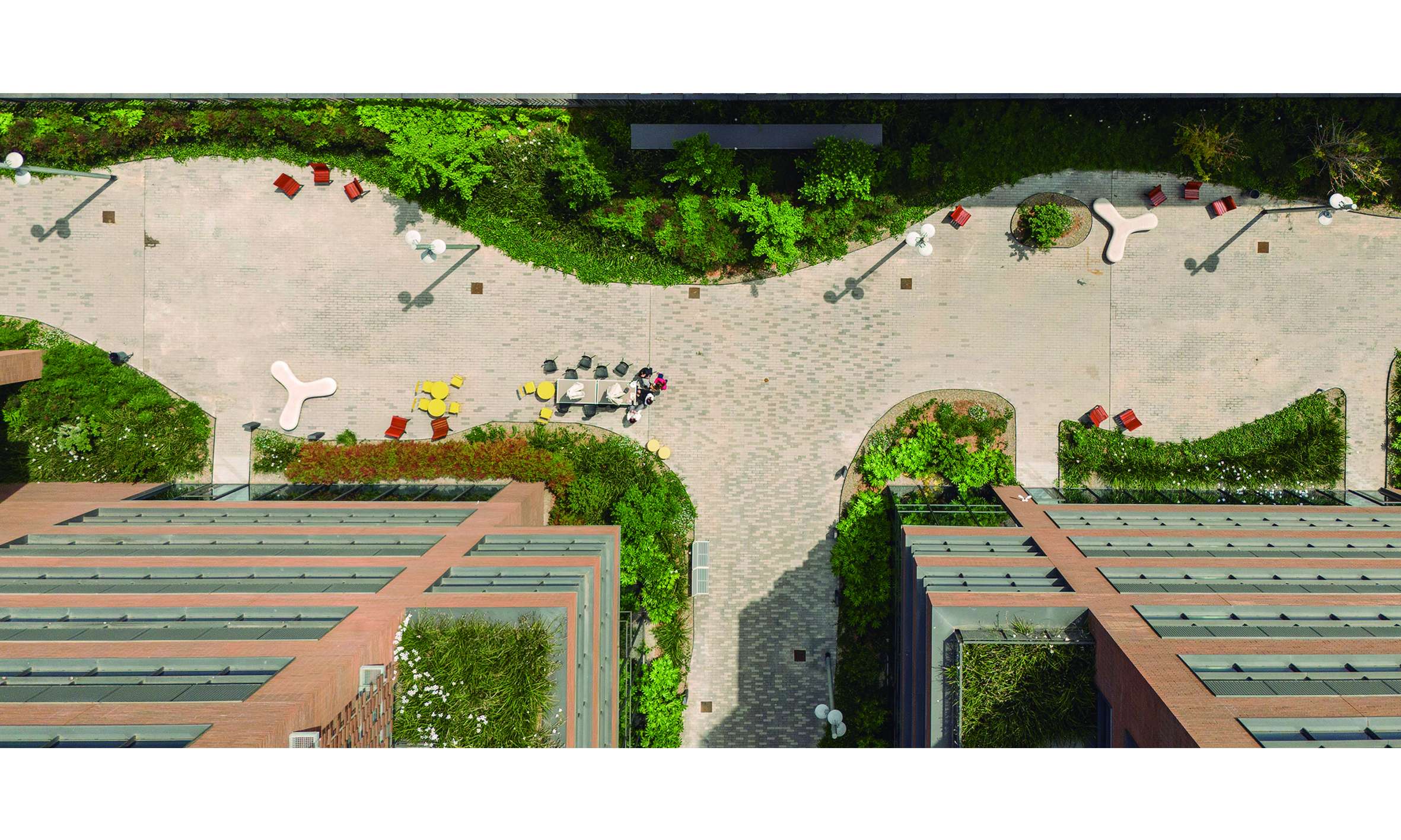
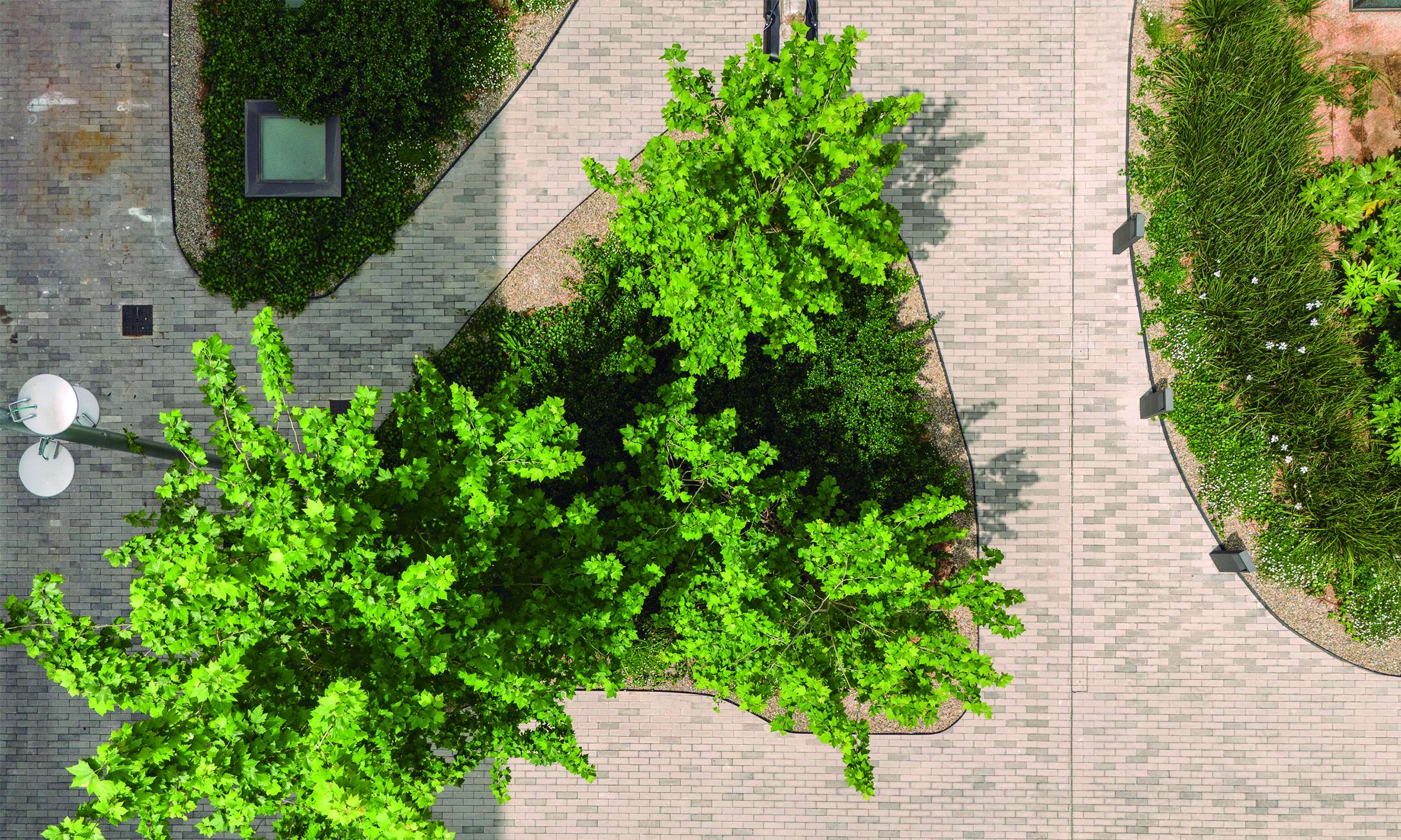
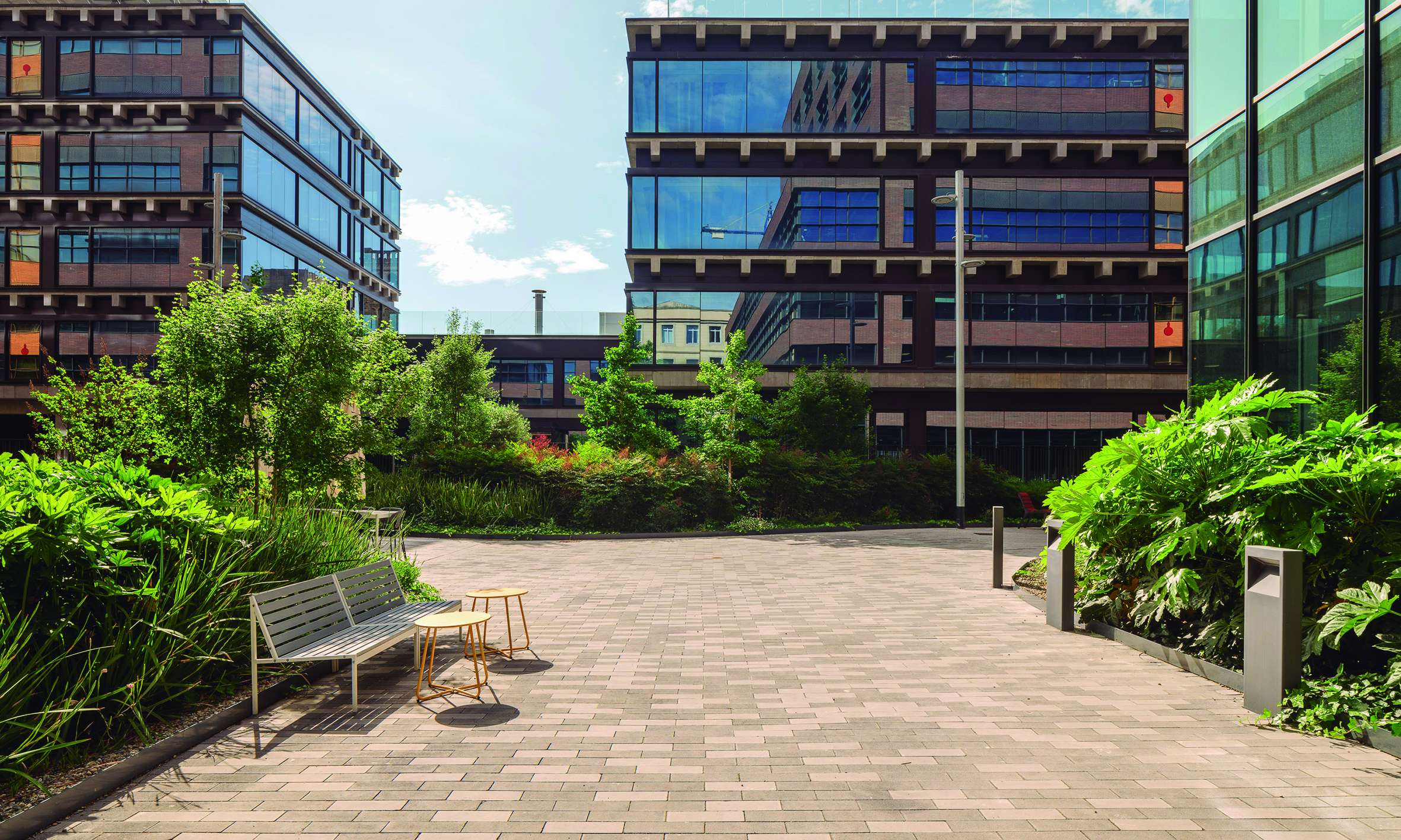
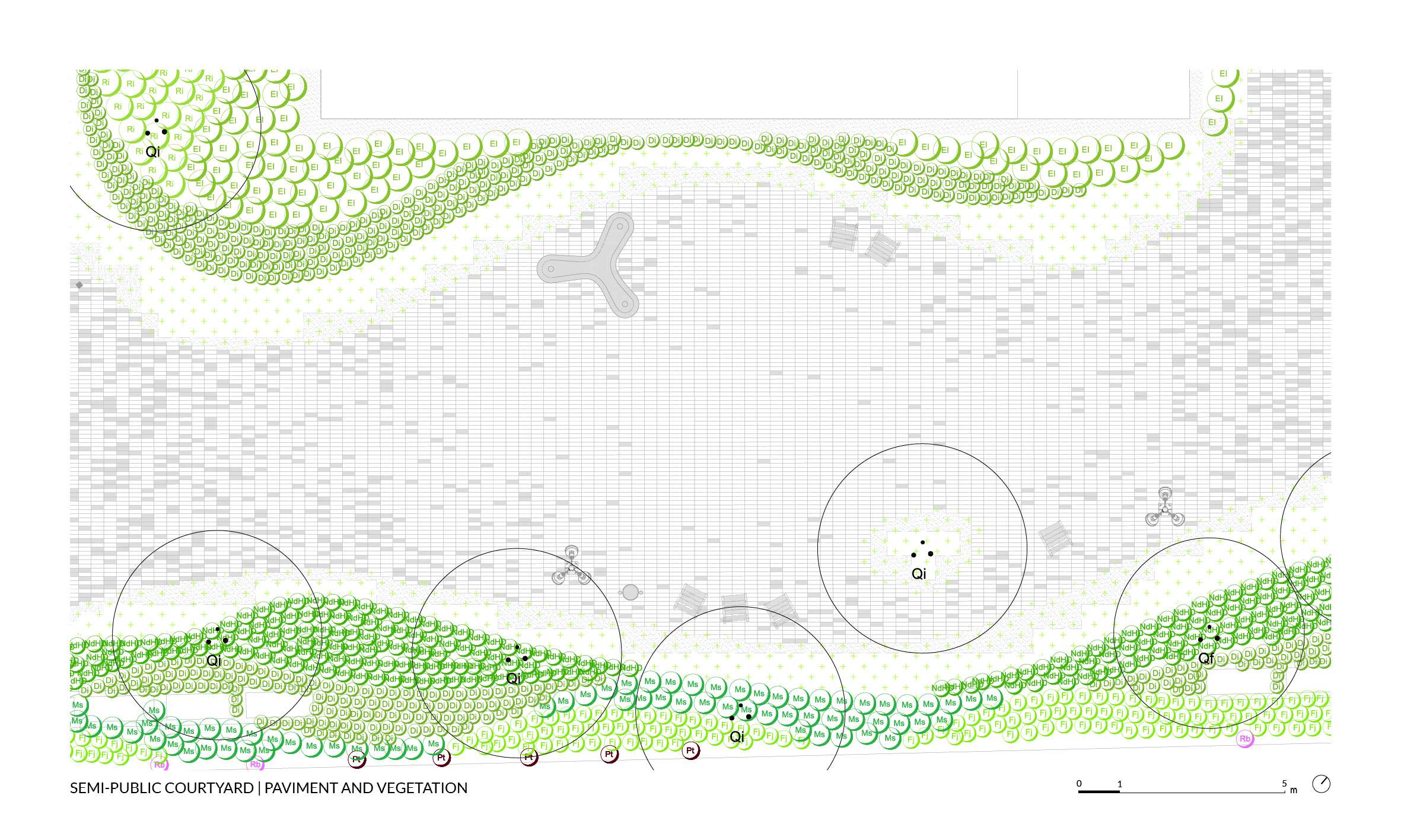
The intervention maximizes green space in order to create the sensation of being immersed in a vegetated environment, rather than merely a simple garden. This is achieved through two key design strategies: the use of shrub and tree vegetation to emphasize the space and create shaded areas, and the minimization of paved surfaces.
The courtyard design is structured around a series of interconnected seating areas—spaces for rest and enjoyment—highlighted by the chosen paving material: a prefabricated concrete paver in two tones. The layout of the pavers emphasizes these rest areas, furnished accordingly, setting them apart from the rest of the environment.
To accommodate the required access for fire and service vehicles, a sequence of small- to medium-scale spaces is created through the gradual widening of circulation paths
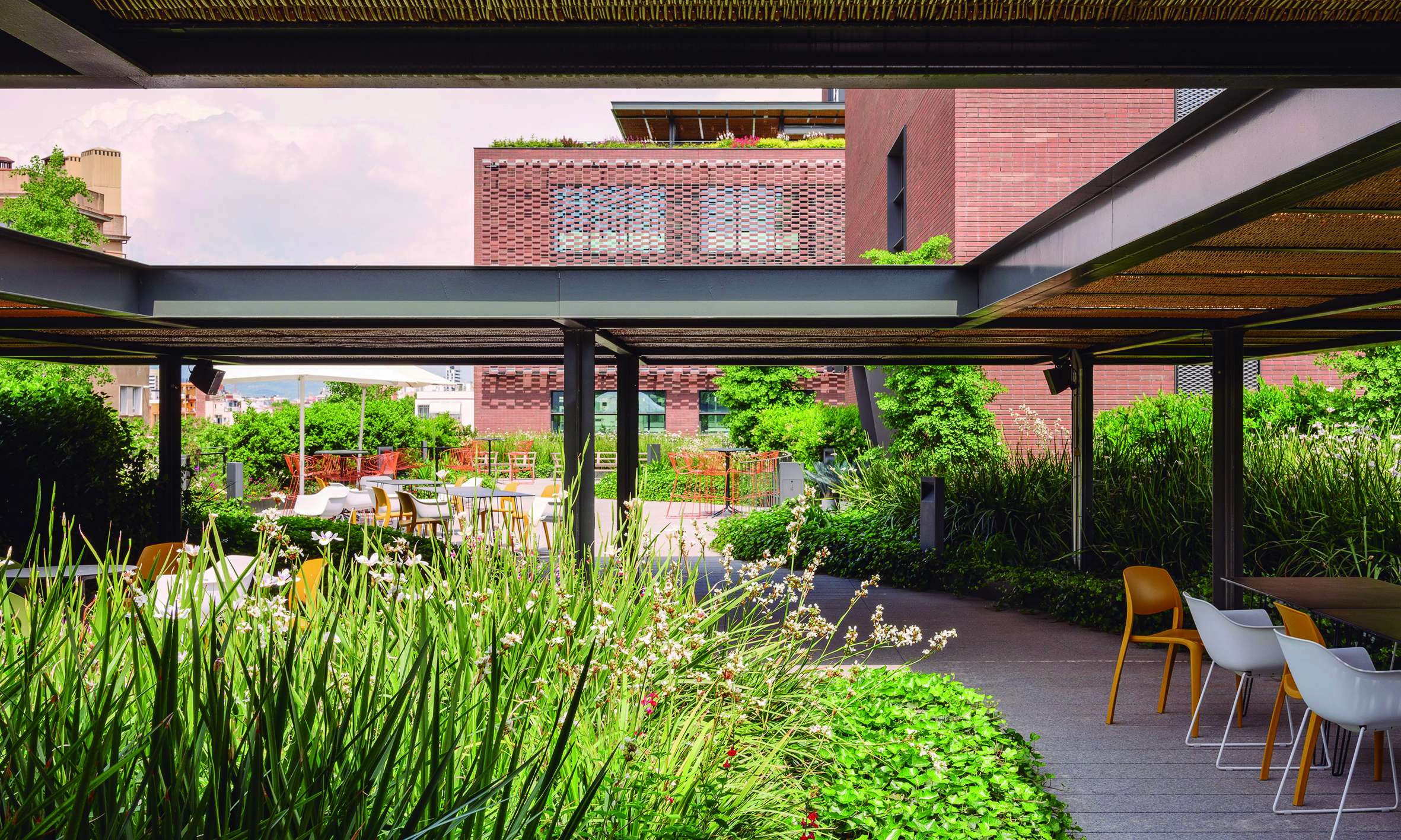
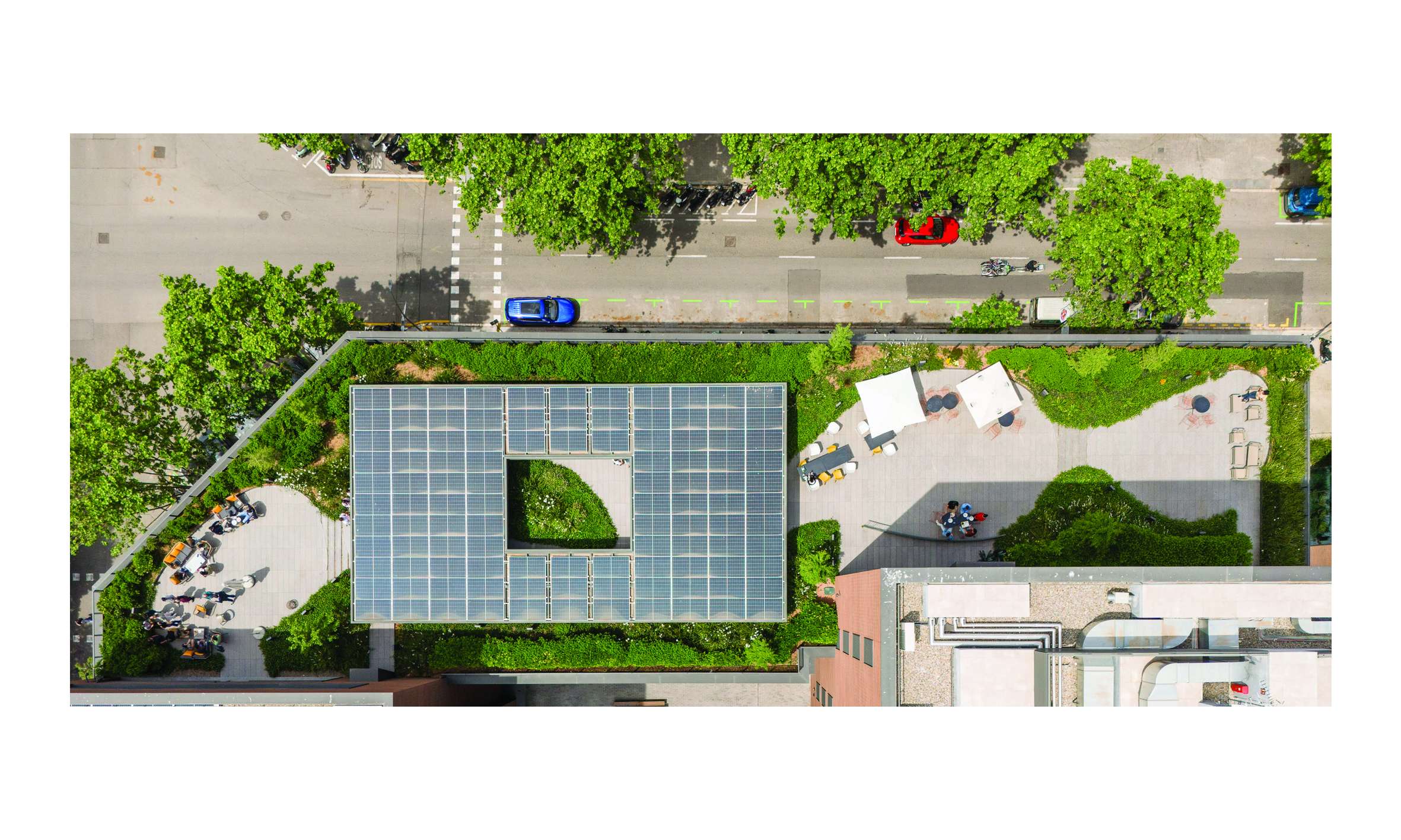
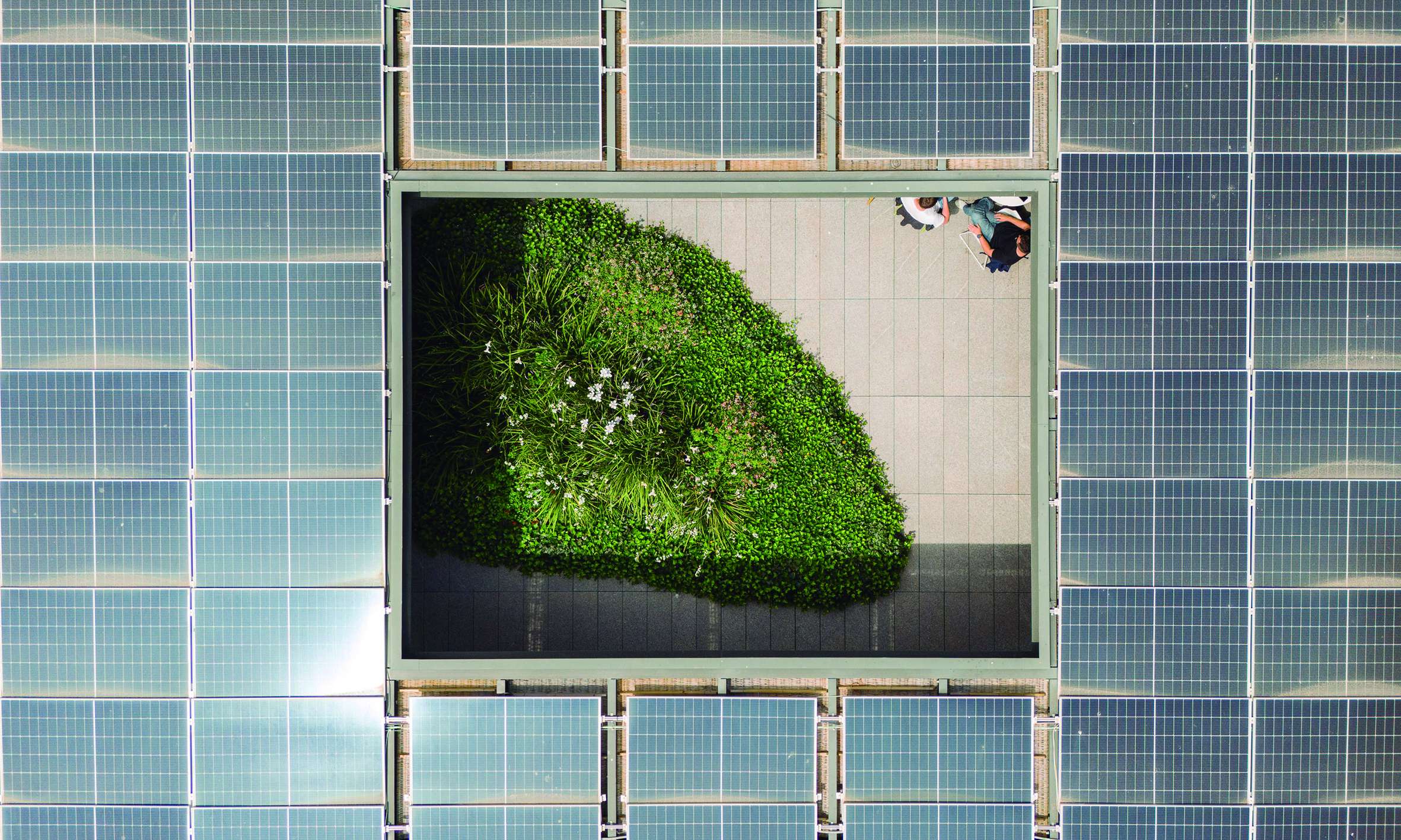
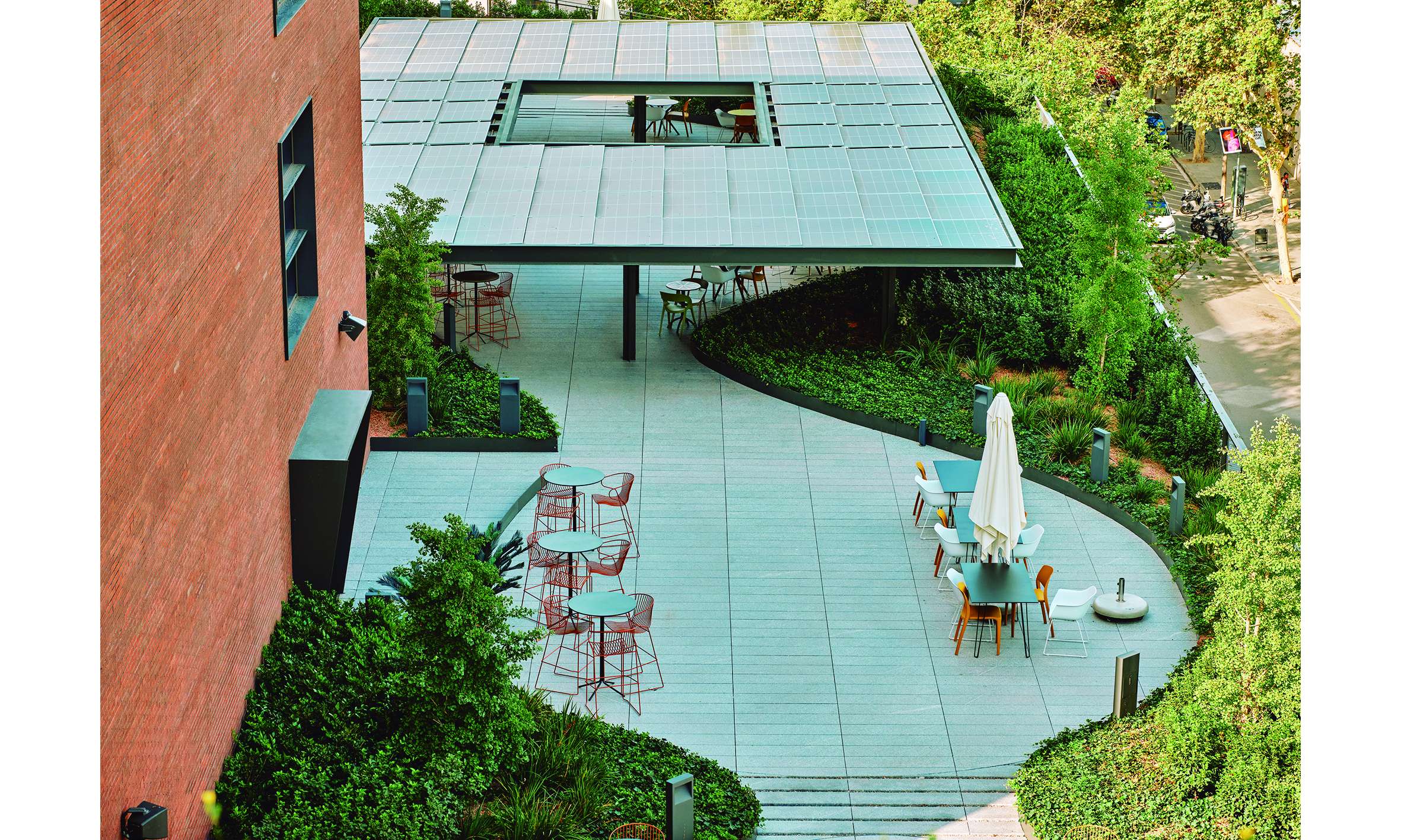
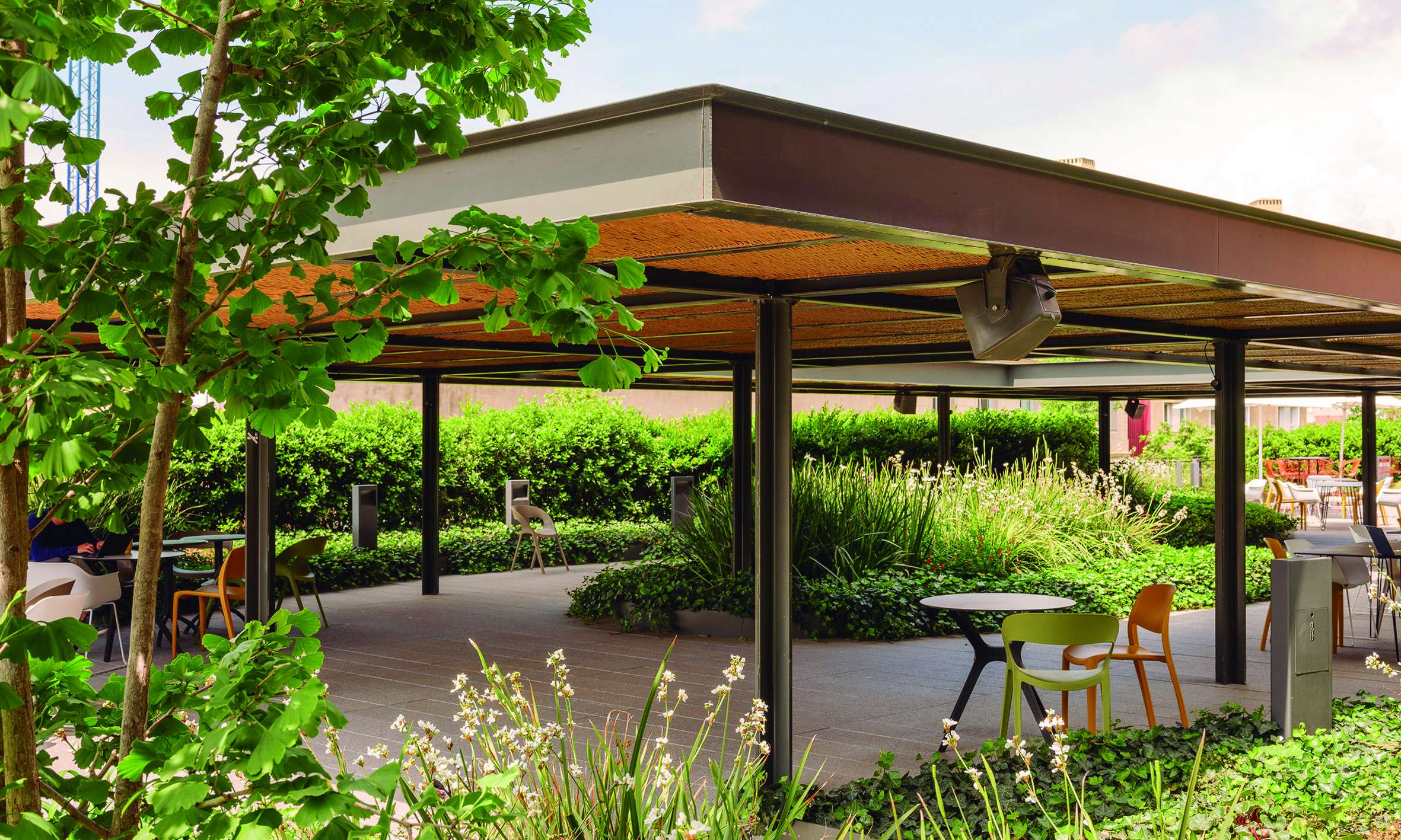
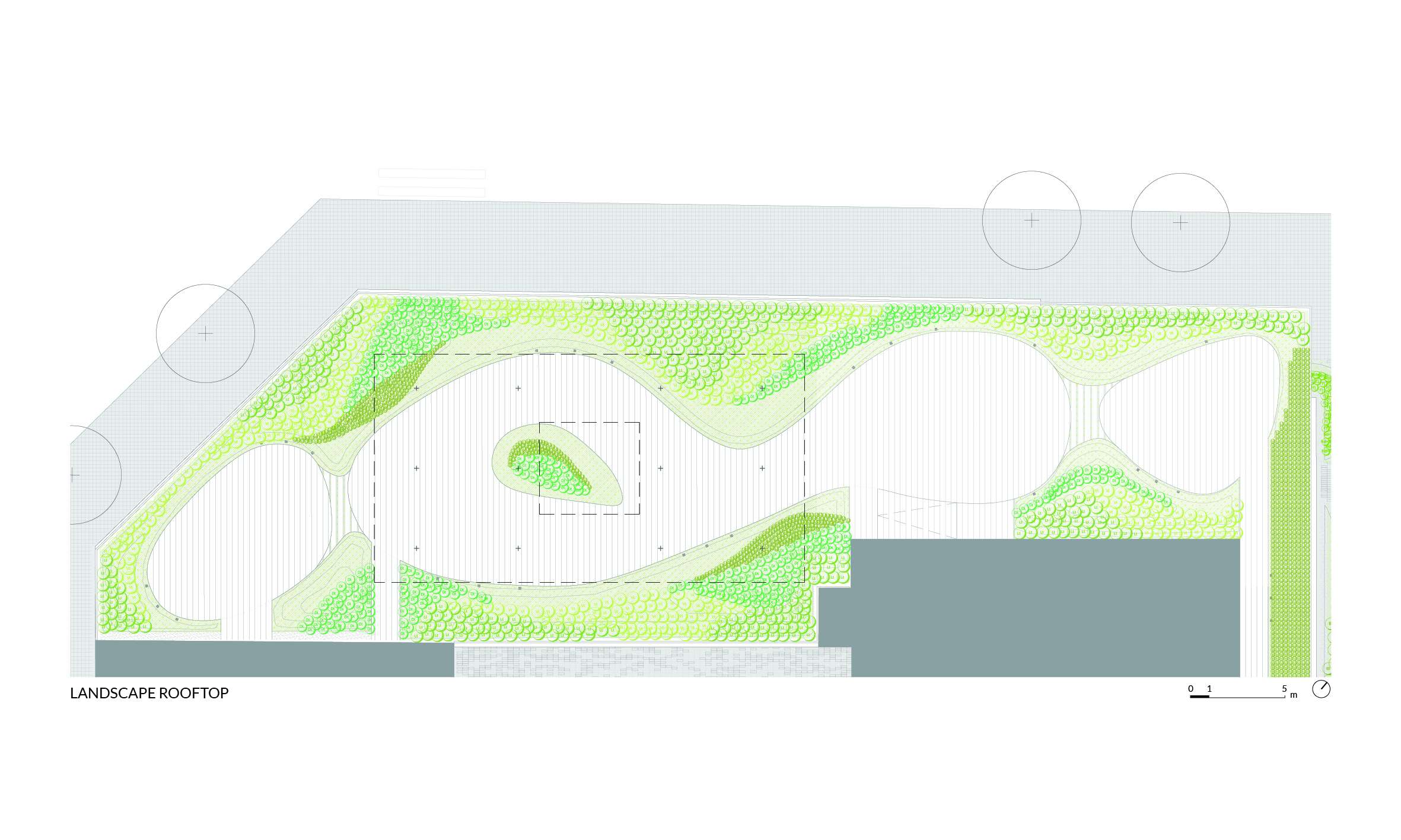
The Rooftops
The project considers the building rooftops, with their privileged views of the city, as a continuation of the interior office spaces. The vegetation in these areas is arranged along the perimeter, visually merging with the surrounding urban greenery, softening the edges of the terraces and emphasizing the garden-like atmosphere.
In this way, from inside the building, a clear and integrated view of the space is achieved, encouraging office users to make use of these areas as places for rest and relaxation, as well as for work.
The Selection of Vegetation: Low Water Consumption and Enhanced Comfort
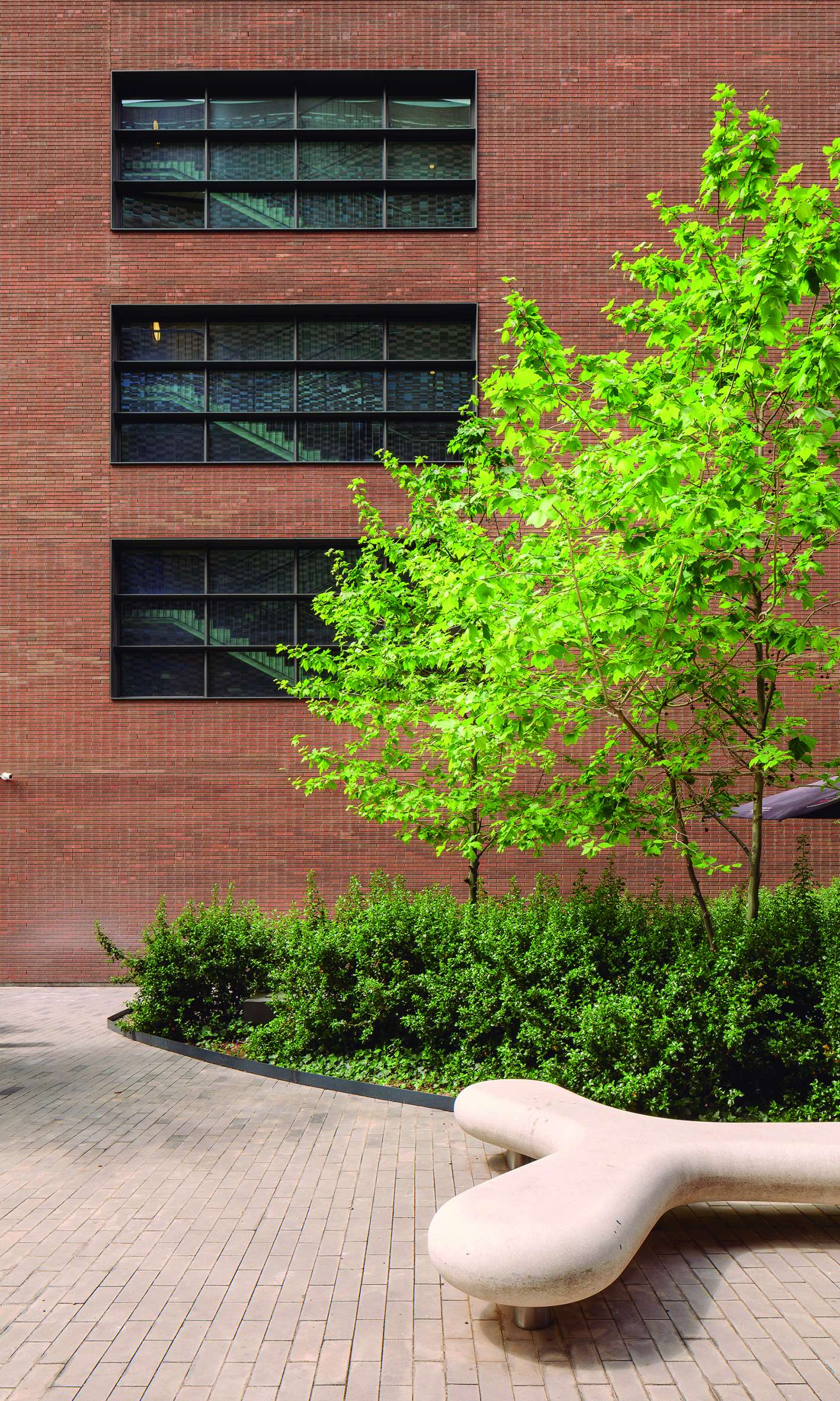
The selection of shrubs and trees focuses on native or well-adapted species with low water needs. No grass lawns have been included; instead, low-growing ground cover species with significantly lower water consumption have been used.
The selected trees are deciduous species, which help reduce solar exposure on paved surfaces during summer while allowing sunlight through in winter, enhancing user comfort. This choice is balanced with the use of evergreen shrubs, which maintain a green base throughout the year, enriched by varying flowering periods.
The plant species are distributed according to their specific sunlight and moisture needs, making use of both the more sheltered, humid areas beneath the rooftops and the more exposed central zones.
