












A New Urban Ecological Highland: Fushan Mountain Park, Qingdao
A New Urban Ecological Highland: Fushan Mountain Park, Qingdao
A New Urban Ecological Highland: Fushan Mountain Park, Qingdao
Implementing large-scale ecological restoration, the Fushan Mountain Park project is an evolving paradigm for sustainable urban stormwater management in China's northern cities and brings a recreation and leisure center in the urban cluster. Fushan Mountain had been a granite quarry with mining pits and later filled with building waste and graveyard. After the large-scale ecological restoration with integrated landscape design methodology, Fushan transforms into a leisure park for urban citizens and becomes a new landmark of Qingdao. This once desolate place now serves as a leisure center closely attaches to the neighborhood and communities, adding a green skyline in Qingdao. Facing the challenges from the polluted urban environment, the boost of population growth, the shortage of natural resources,
Project Narrative
Overview
Implementing large-scale ecological restoration, Fushan Mountain Park is an evolving paradigm for sustainable urban stormwater management in China's northern cities that integrates recreational, ecological, and cultural resources together in the city of Qingdao. Fushan Mountain Park is a former granite quarry with mining pits which were later filled with urban building waste and a graveyard. After the team's large-scale ecological restoration with integrated landscape reclamation methods, Fushan was transformed into a multi-use public park that performs both as a place for people generously connected to the neighborhoods and a territory for ecosystem infrastructure. Facing the challenges from the polluted urban environment, the boost of population growth, the shortage of natural resources,
Planning and Design
Background
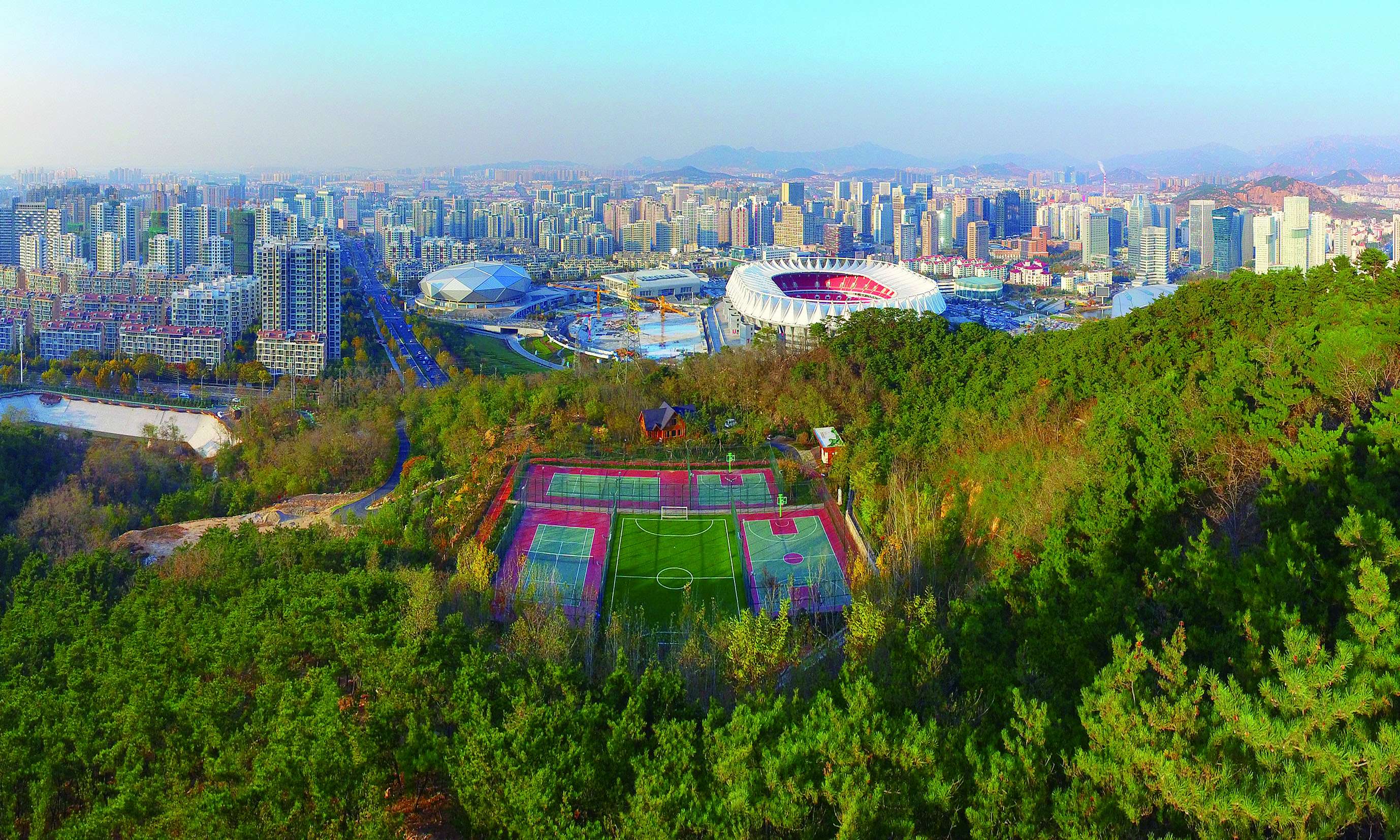
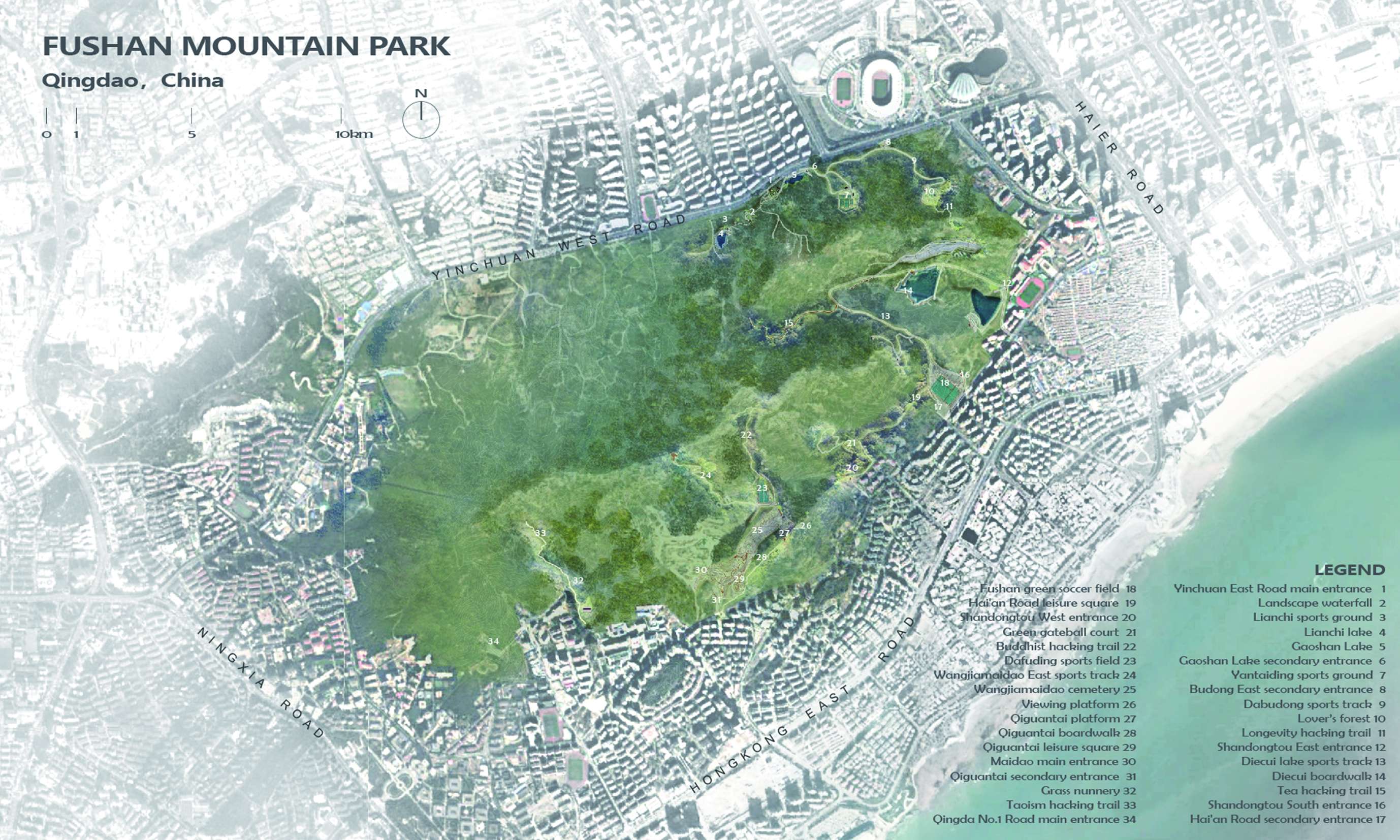
Fushan Mountain, covering an area of 7.5 square kilometers, is known as the highest mountain in Qingdao City, Shandong Province, China with a peak elevation of 368 meters. It provides nice panoramic views over the city.
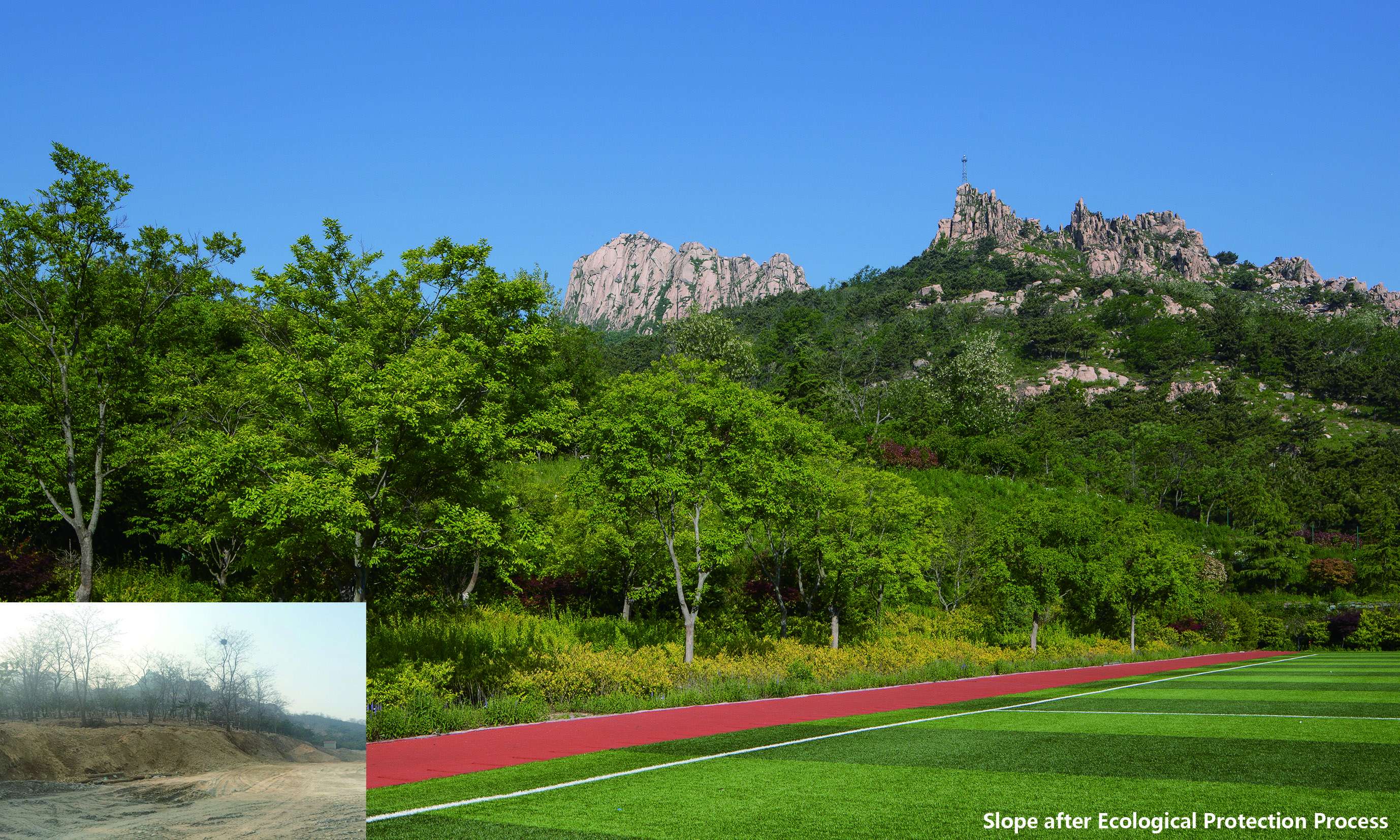
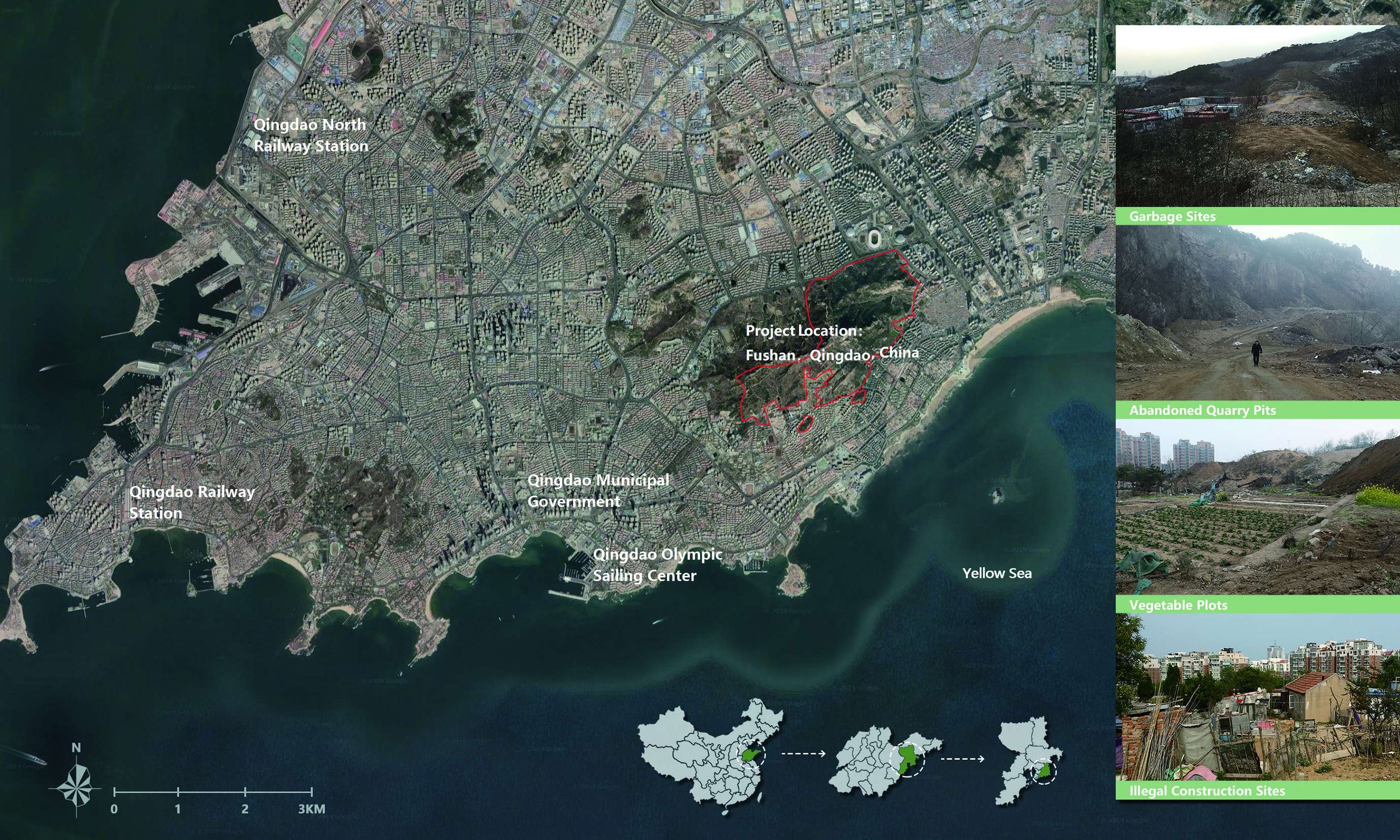
In recent years, with urban expansion, Fushan Mountain area has been evolving into a new urban center of Qingdao. The massive urbanization caused considerable damage to the natural environment: Fushan lost lush green vegetation and gurgling mountain streams, and was filled with illegal construction, desolated graves, and garbage sites. Such destruction of mountain vegetation resulted in severe soil erosion and unstable ecological system; Thus it is urgent to restore the eco-environment and provide residents with green activity space.
Combining the ecological restoration and the park redesigning in the urban area, the design team embraced the ideals of an integrated design methodology to convert Fushan Mountain into an urban green lung space, offering a harmonious and sustainable center for urban health and recreation.
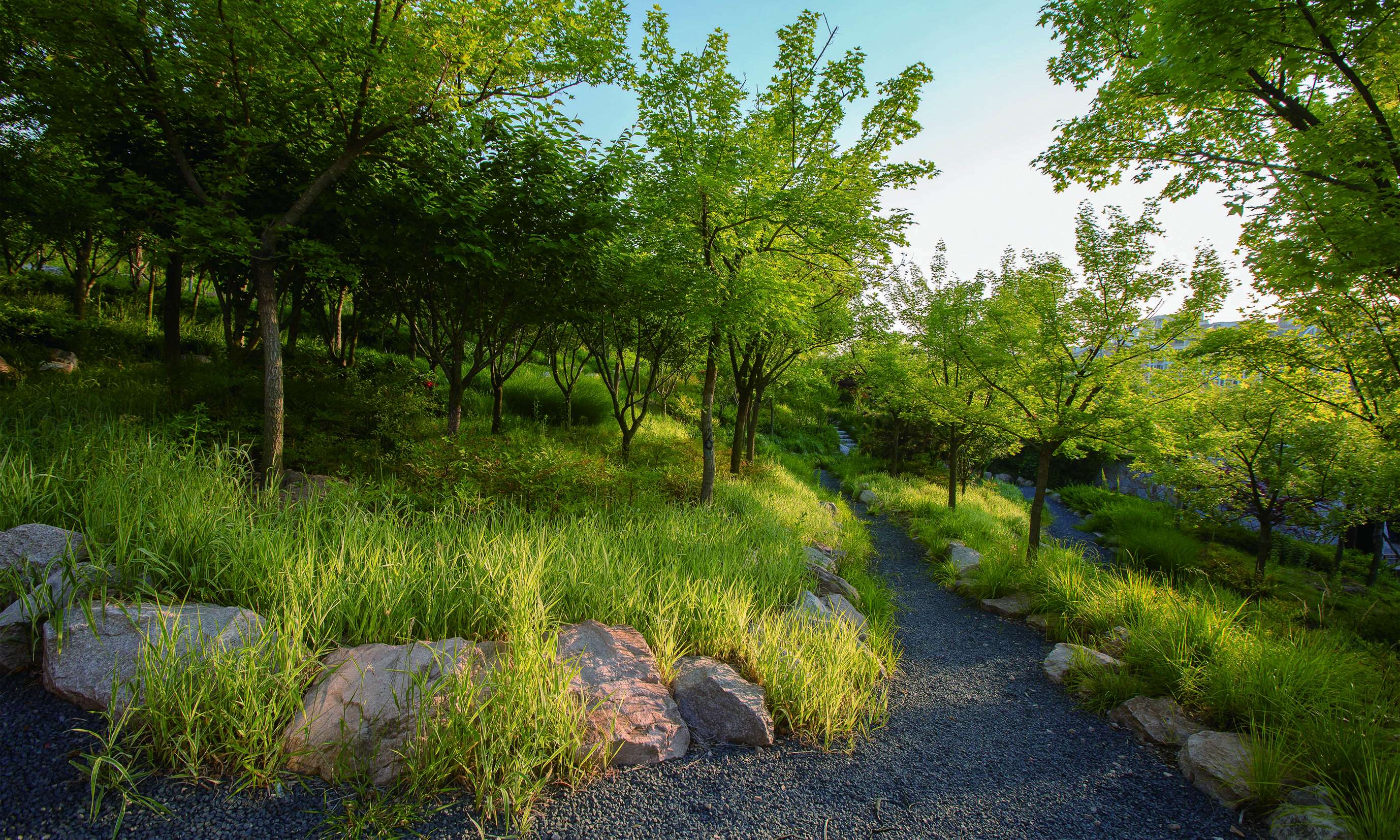
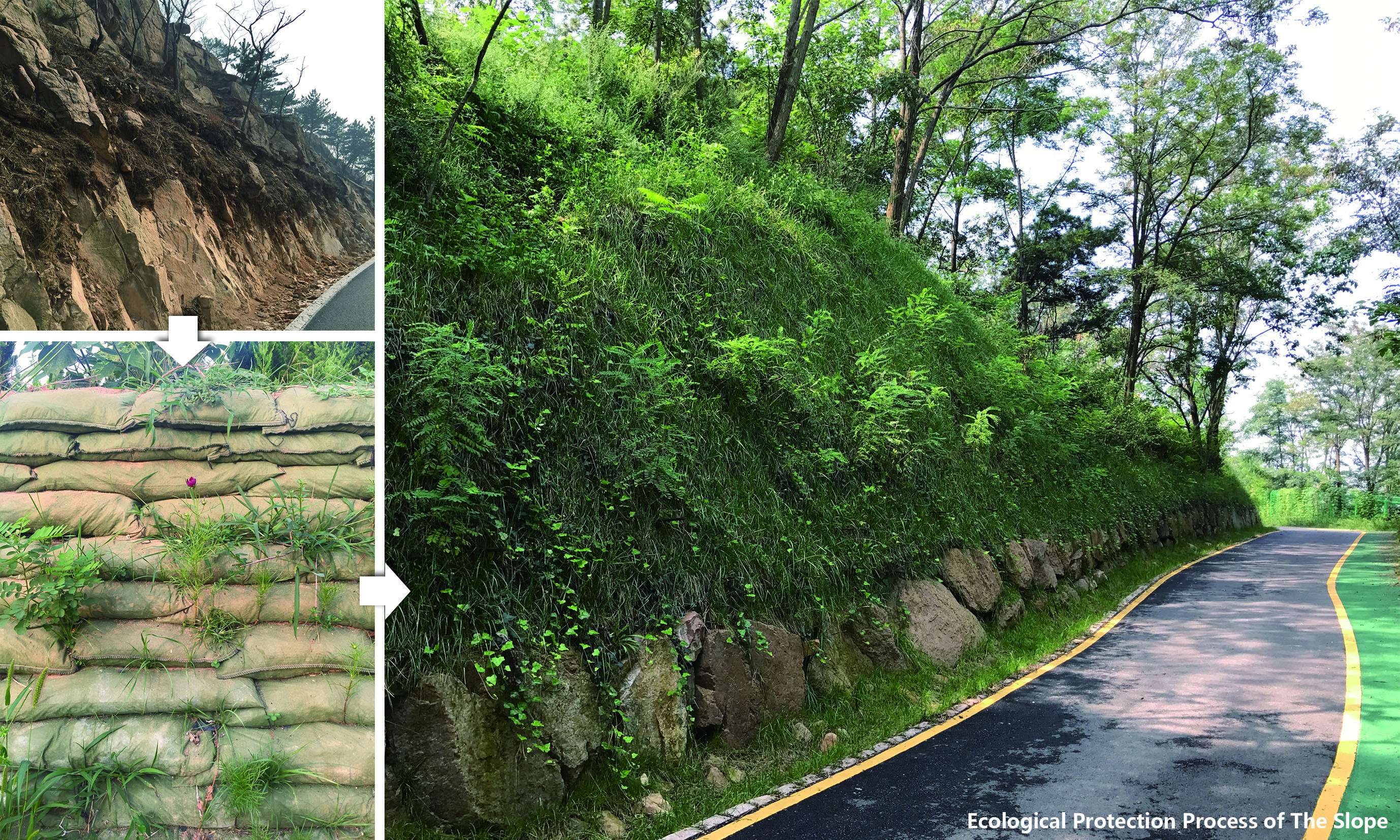
Reproducing the natural habitat by reforestation: the rapid urban expansion outpaces the regeneration of eco-environment and puts Fushan Mountian in jeopardy. The primary task for the designers to rehabilitate the original natural habitat. In the design, 167 species of trees, shrubs, and grasses were employed and up to 90% of them were native-species. Designers arrange different types of plants in response to the elevation with a multi-layered approach to ensure the resistance and stability of communities. There are 98,092 trees, shrubs and grasses, and 63-hectare reforestation area in total, accounting for 19.1% of the total mountain area. And the ecological restoration area accounts for about 80% of the entire area of the mountain. In the process, designers optimized the approach to address ecological destruction problems. For instance, spraying technique was adopted to reinforce the soil and deal with vegetation destruction and soil erosion caused by steep soil ridges arising from road construction. Thanks to a multi-layered terrace with ecological planting bag technique, designers replaced the traditional solid retaining wall and addressed the large height difference issue at the field and greatly improved ecological conditions and aesthetic effect.
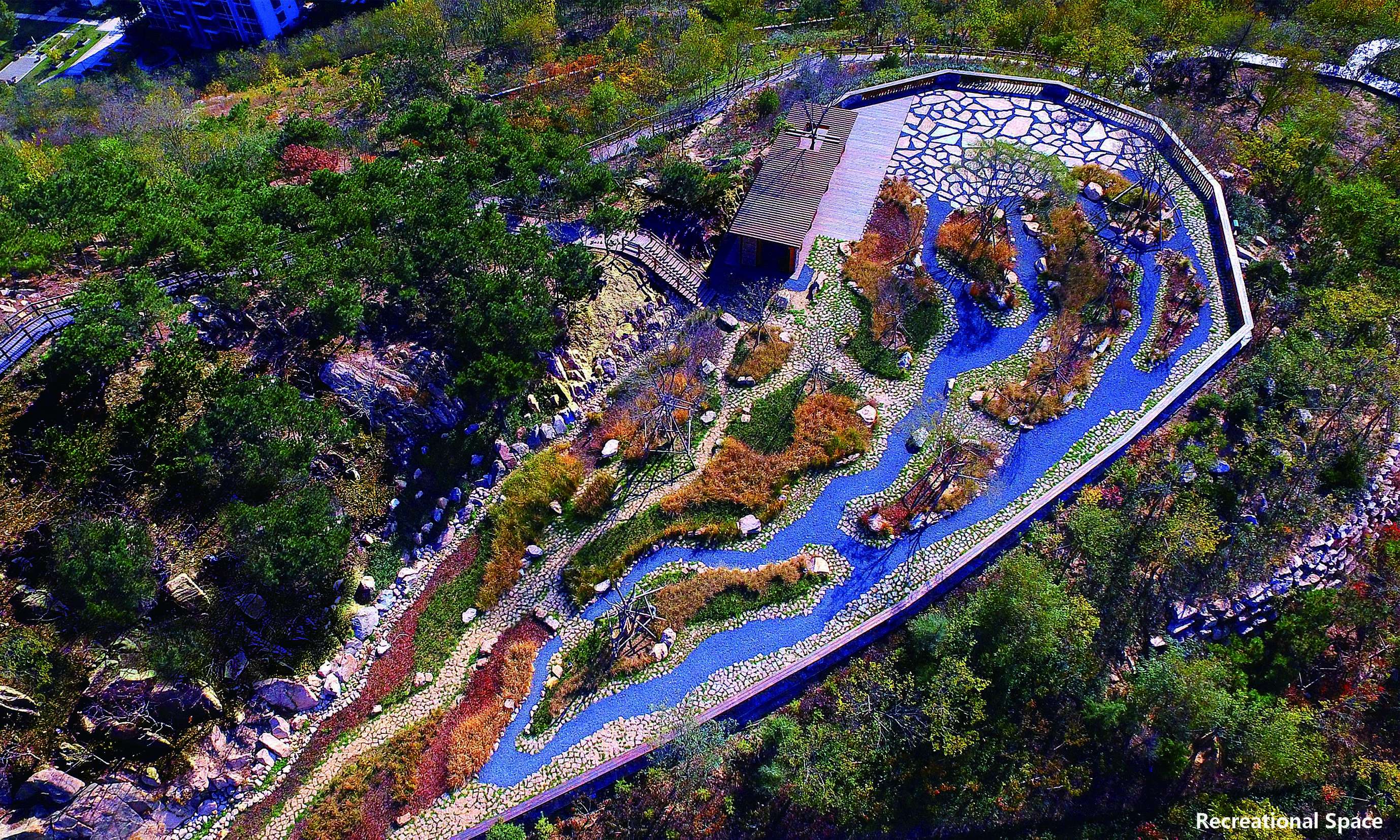
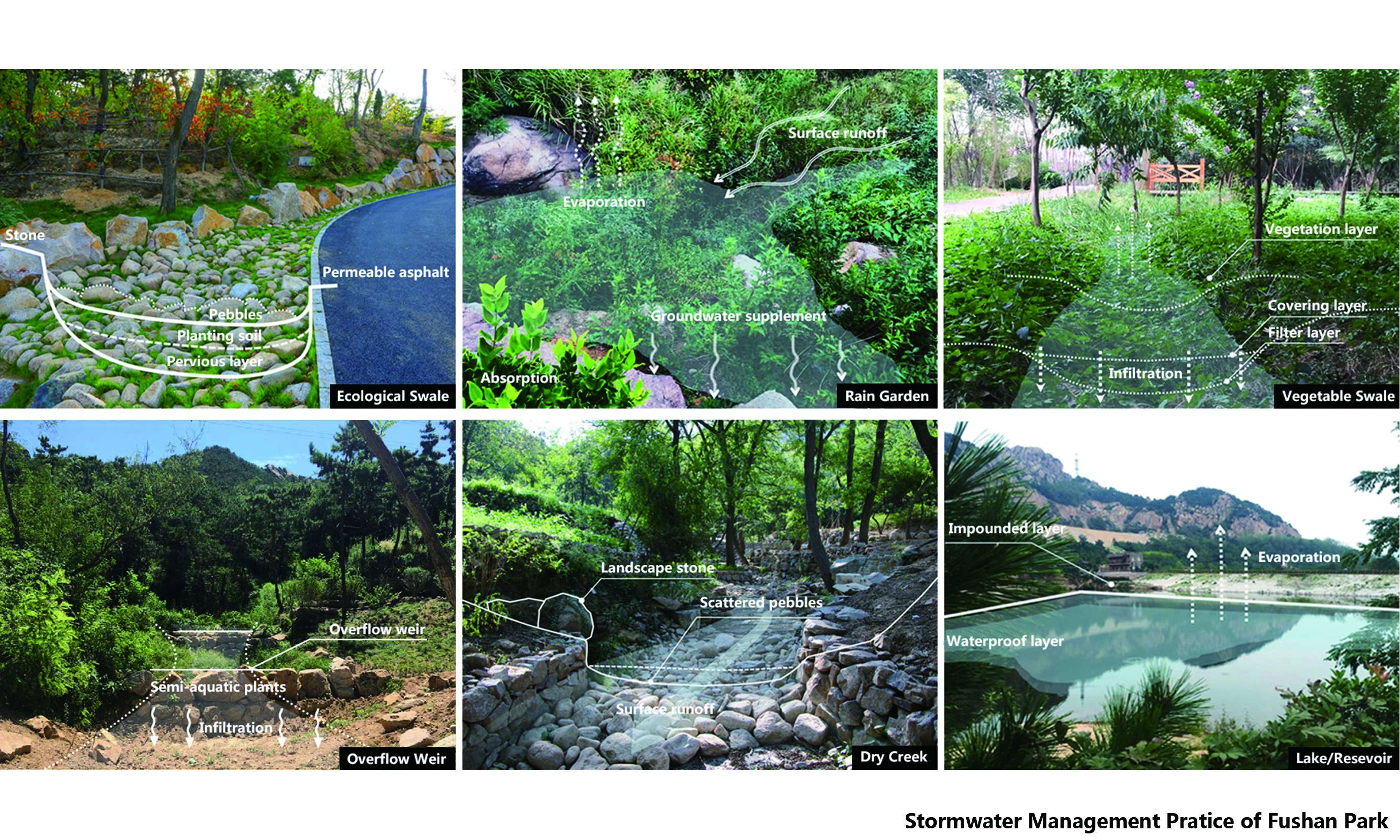
Building the green sponge by stormwater management:confronted with severe soil erosion, gully in the hillside after heavy rain and muddy road surfaces, designers made the following efforts to build a green sponge area in the mountain: performed dredging from the original natural surface runoff network, and employed stormwater management techniques to retain runoff and protect water source for a complete water system. Designers also renovated the partial catchment areas into dry creek beds and rain gardens to enrich the landscape and preserve rainwater resources. The design arranged vegetated swale along one side of the road to maximize the sinking of rainwater and replenish the mountain groundwater while satisfying flood discharge in case of any rainstorm. Designers kept curbs at the same height of the road and dug deep grooves to increase Siphon effect on the basis of natural rainwater gravity overflow so as to divert the rainwater to the maximum extent. The design grassed ditches at slope edge to intercept ground rainwater in case of rainstorm and built natural overflow weir with local large stones and block stones in the main catchment corridor and grew semi aquatic plants to reduce the flow rate of rainwater, prevent the mountain soil erosion and retain sediments carried by the mountain torrent, purify water body and form a landscape of creeks and small waterfall. The design finally converged surface flows into three reserves at the foot of the mountain to supply water for maintenance and irrigation. The design grassed ditches at slope edge to intercept ground rainwater in case of rainstorm and built natural overflow weir with local large stones and block stones in the main catchment corridor and grew semi aquatic plants to reduce the flow rate of rainwater, prevent the mountain soil erosion and retain sediments carried by the mountain torrent, purify water body and form a landscape of creeks and small waterfall. The design finally converged surface flows into three reserves at the foot of the mountain to supply water for maintenance and irrigation. The design grassed ditches at slope edge to intercept ground rainwater in case of rainstorm and built natural overflow weir with local large stones and block stones in the main catchment corridor and grew semi aquatic plants to reduce the flow rate of rainwater, prevent the mountain soil erosion and retain sediments carried by the mountain torrent, purify water body and form a landscape of creeks and small waterfall. The design finally converged surface flows into three reserves at the foot of the mountain to supply water for maintenance and irrigation. prevent the mountain soil erosion and retain sediments carried by the mountain torrent, purify water body and form a landscape of creeks and small waterfall. The design finally converged surface flows into three reserves at the foot of the mountain to supply water for maintenance and irrigation. prevent the mountain soil erosion and retain sediments carried by the mountain torrent, purify water body and form a landscape of creeks and small waterfall. The design finally converged surface flows into three reserves at the foot of the mountain to supply water for maintenance and irrigation.
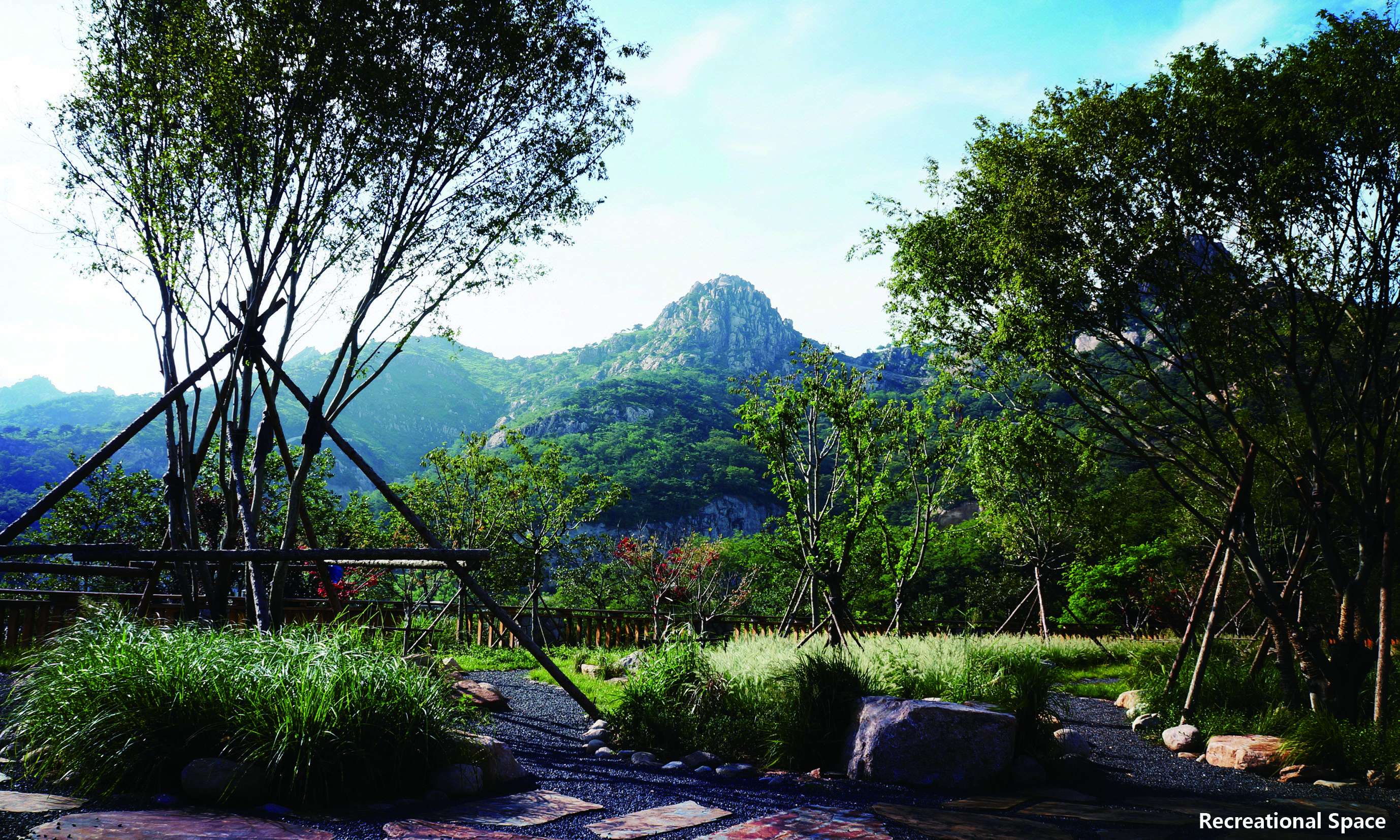
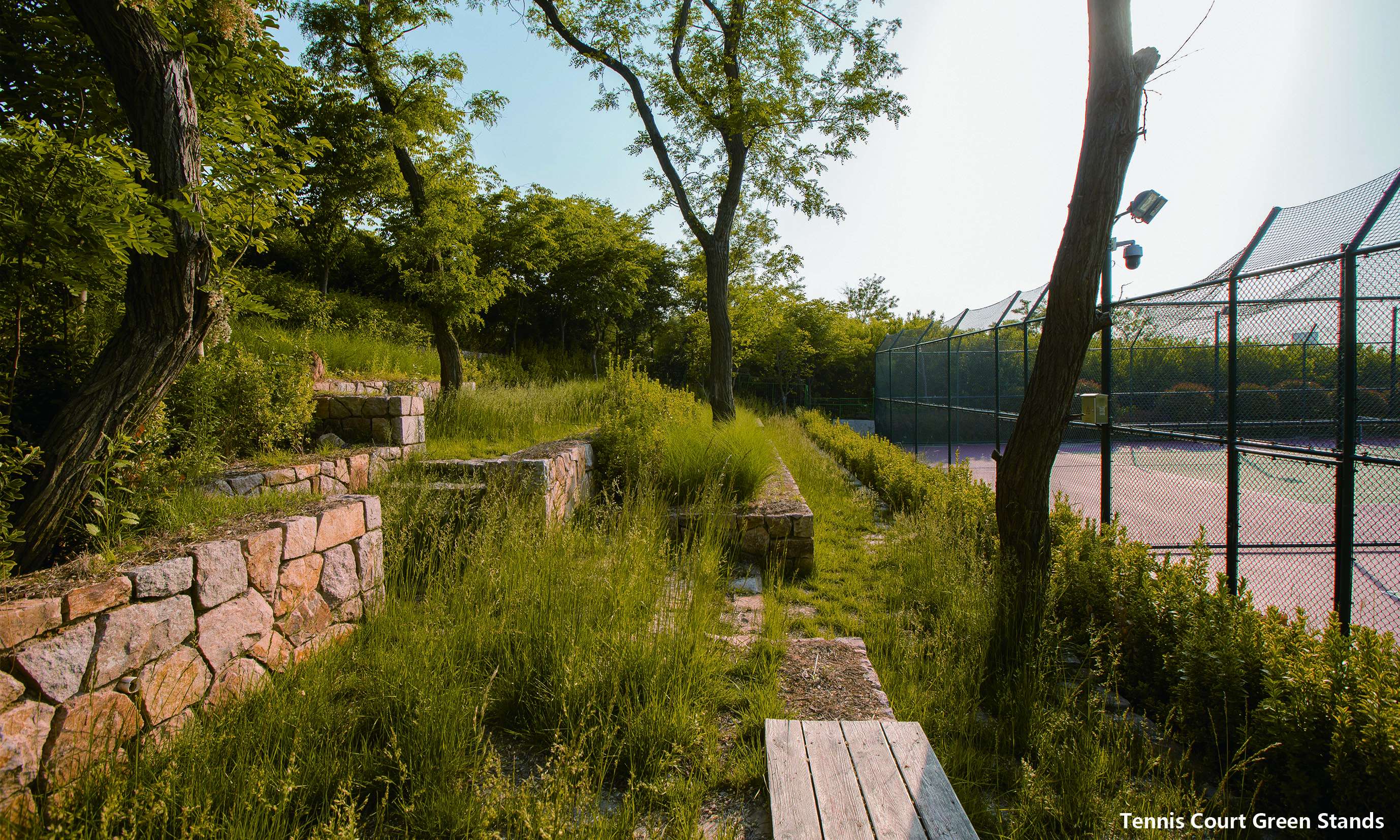
Repairing mining pits and building a recreation park: once a famous Granite mining site in China, Fushan was left with many abandoned mining pits since the country banned stone mining. Designers took advantages of the original mining sites to set 5 zones for 16 sports courts, serving football, basketball, gateball and other games and made use of the waste stones from the quarry to construct green stands for the audience. Furthermore, Designers transformed the six fire-fighting accesses into sports tracks with layered plant on both sides. This design not only satisfying fire-fighting functions but offering runners a pleasant exercising place. Designers also set up natural playgrounds for kids, and typical rest and leisure areas for the aged, exemplifying the best for a human-ecological park.
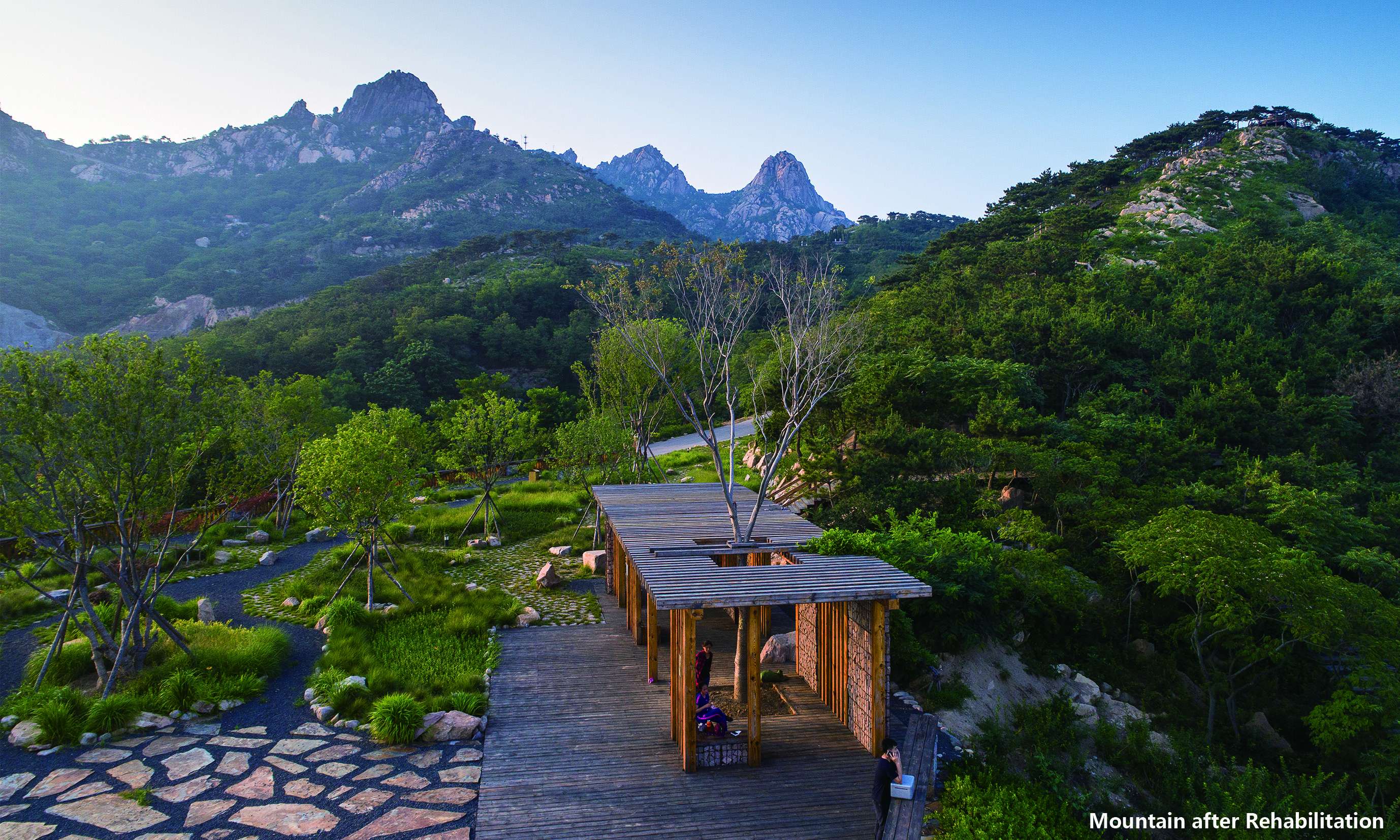
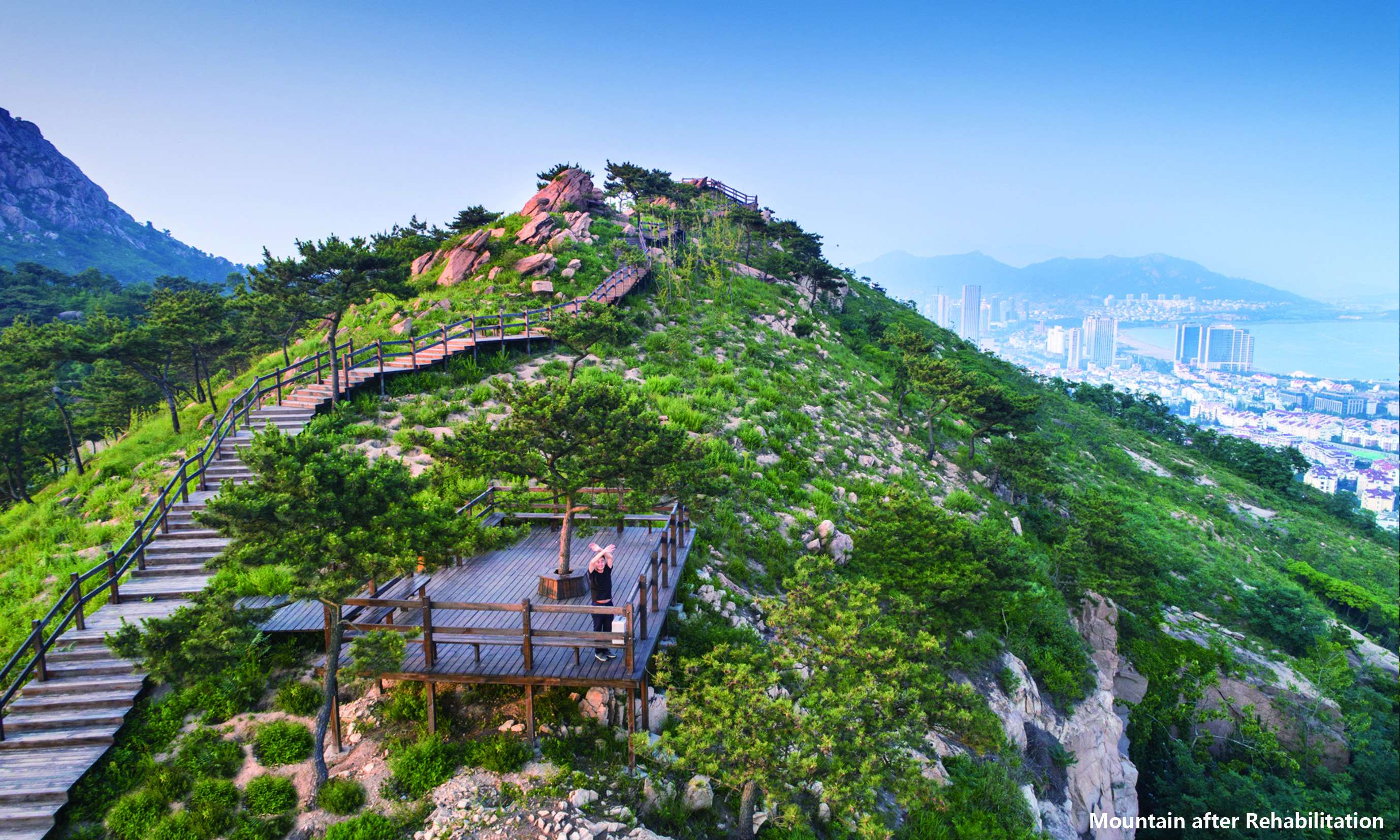
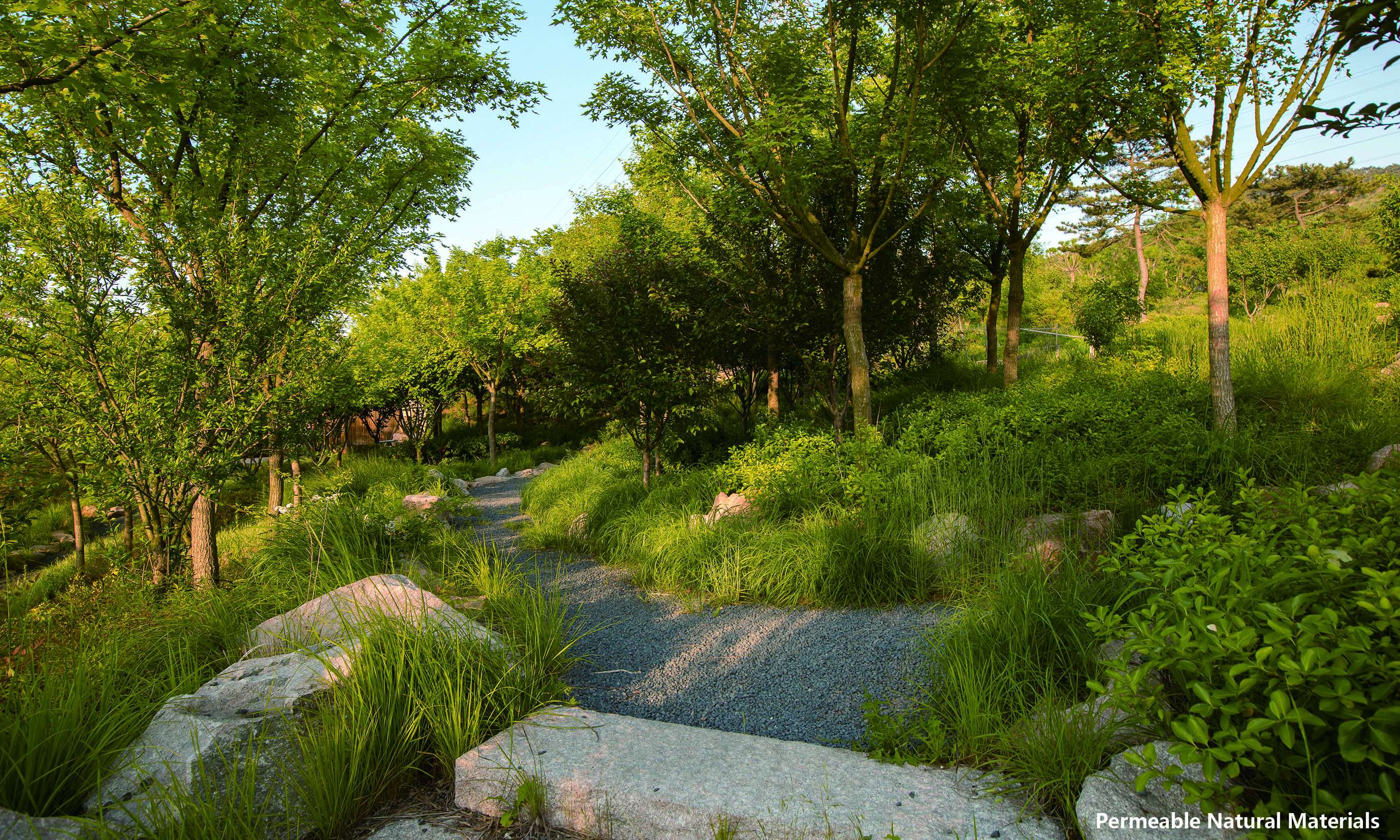
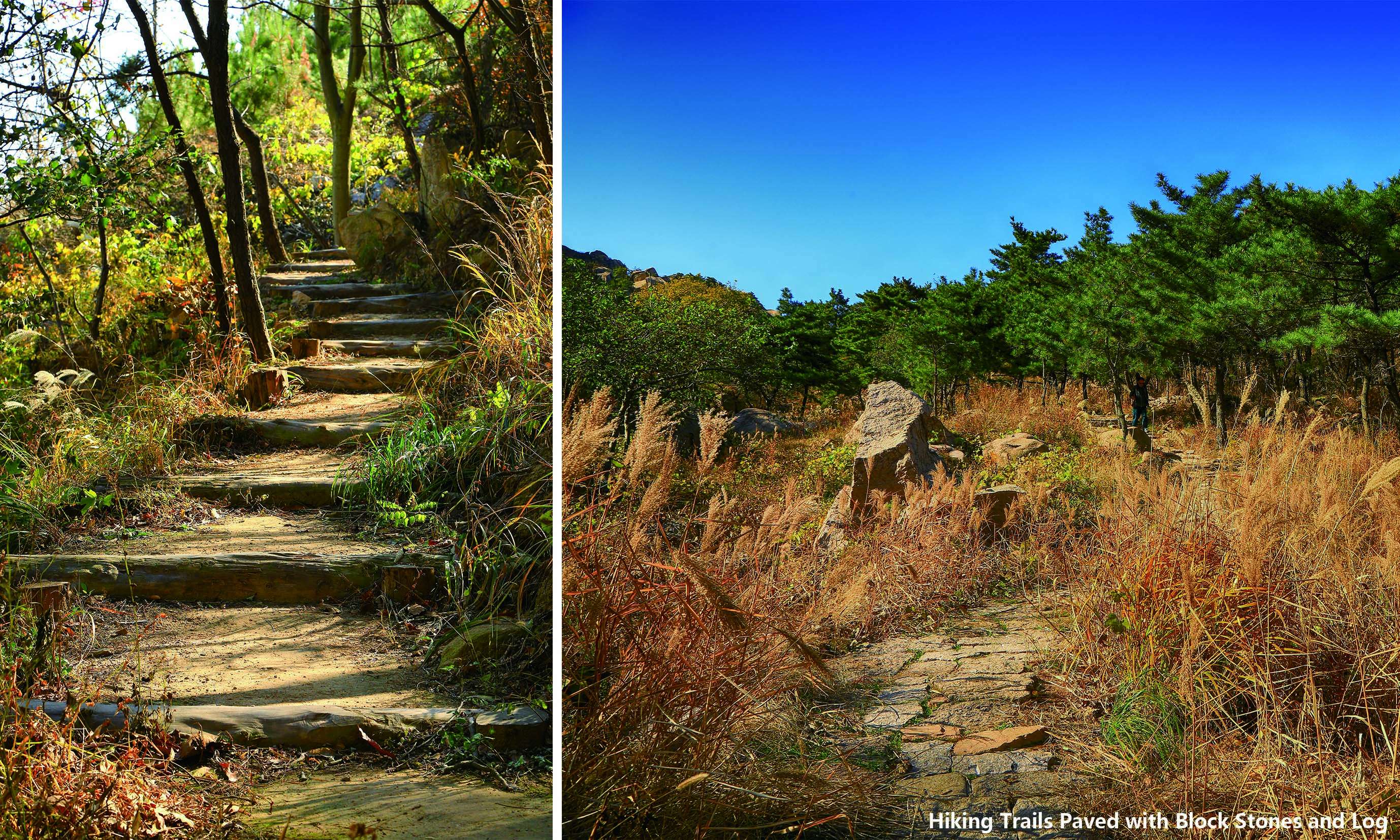
Building a landscape blended with nature by reconstructing wastelands:many wastelands and building wastes were left on the mountain after illegal buildings were removed. Re-using many salvaged materials, designers built 4 leisure sections and 3 viewing platforms. They were paved entirely with permeable natural materials as stone, flagstone, and aggregate, and equipped with corridors, benches, sports facilities made of logs, block stones, Corten steel plates and other ecological, environment-friendly, durable and low-maintenance materials without any coating but the log cover. Meanwhile, employing the original mountain trails, designers followed the Chinese traditional gardening ideology as “Imitation of Nature”, instructed the workmen to pave mountain-climbing steps and walkways with block stones, log, and other natural materials, and further took advantage of the original topography and local materials, detoured existing trees, reserved the original boulder as benches. In a nutshell, the design of the recreation areas and mountain-climbing display the harmonious eco-human system.
Designing and constructing human-ecological cemeteries:transform the local cemeteries is an essential task for this design. Family cemetery in Fushan Mountain built with high stone walls and many grave mounds with barren vegetation, not only offering a gloomy atmosphere but bringing environmental issues by burning joss paper in ancestor worship. However, the traditional perception of a cemetery as guarding health and wealth and avoiding relocation of the family cemetery is a great challenge for designers. The designers should transform and upgrade the cemetery while respecting the tradition and custom. Facing the difficult negotiations and seeking a comprehensive agreement with government and residents, designers propose the method of transformation of a garden-type cemetery at the original site: without relocation of the original tombs, removing the retaining walls disharmonious with the landscape and renovating with ecological bags; planting trees, shrubs and ground-cover flowers in and around to build a garden-type evergreen cemetery landscape; and encouraging to replace the tradition burning joss paper with wreath-laying ceremony to enhance the ecological protection awareness. This unique and creative designing embraced sustainable development principles and the appreciation of social attachment and cultural value.
Summary
Since its completion, Fushan Mountain Park is the city's major eco-environment infrastructure and relax and rest place for the urban citizens. It is a design paradigm embracing integrated methodology with sustainable ideals: ecological restoration, green sponge, stormwater management, Rain Gardens, leisure and visitors' view open spaces, etc. From past desolate area into today's new green landmark, Fushan project provides a beautiful, vital, sustainable, resilient green public space in the urban clusters in Qingdao.
In August 2019, the Fushan Mountain Park project won the 2019 British Landscape Industry Association (BALI) International Award
In August 2019, the Fushan Mountain Park project won the 2019 IFLA International Landscape Architects Federation Asia Pacific Regional Park & Open Space Design Honor Award
In October 2019, the Fushan Mountain Park project the second prize of the 2019 China Landscape Architecture Society Science and Technology Award Planning and Design Award domestic award
